How to Implement an eCommerce PIM to Scale Your Shopify Catalog
Master your product data model, centralize attributes, and eliminate CSV chaos with an effective eCommerce PIM strategy.
Jan 27, 2026
Learn to diagnose, prioritize, and fix product feed errors to improve ROAS for Shopping and Performance Max campaigns.

A quick diagnosis of the Google Shopping feed allows you to identify errors that reduce impressions and sales, prioritizing them according to impact and effort. Priority is defined by how many items are blocked or de-indexed and how long the catalog is affected.
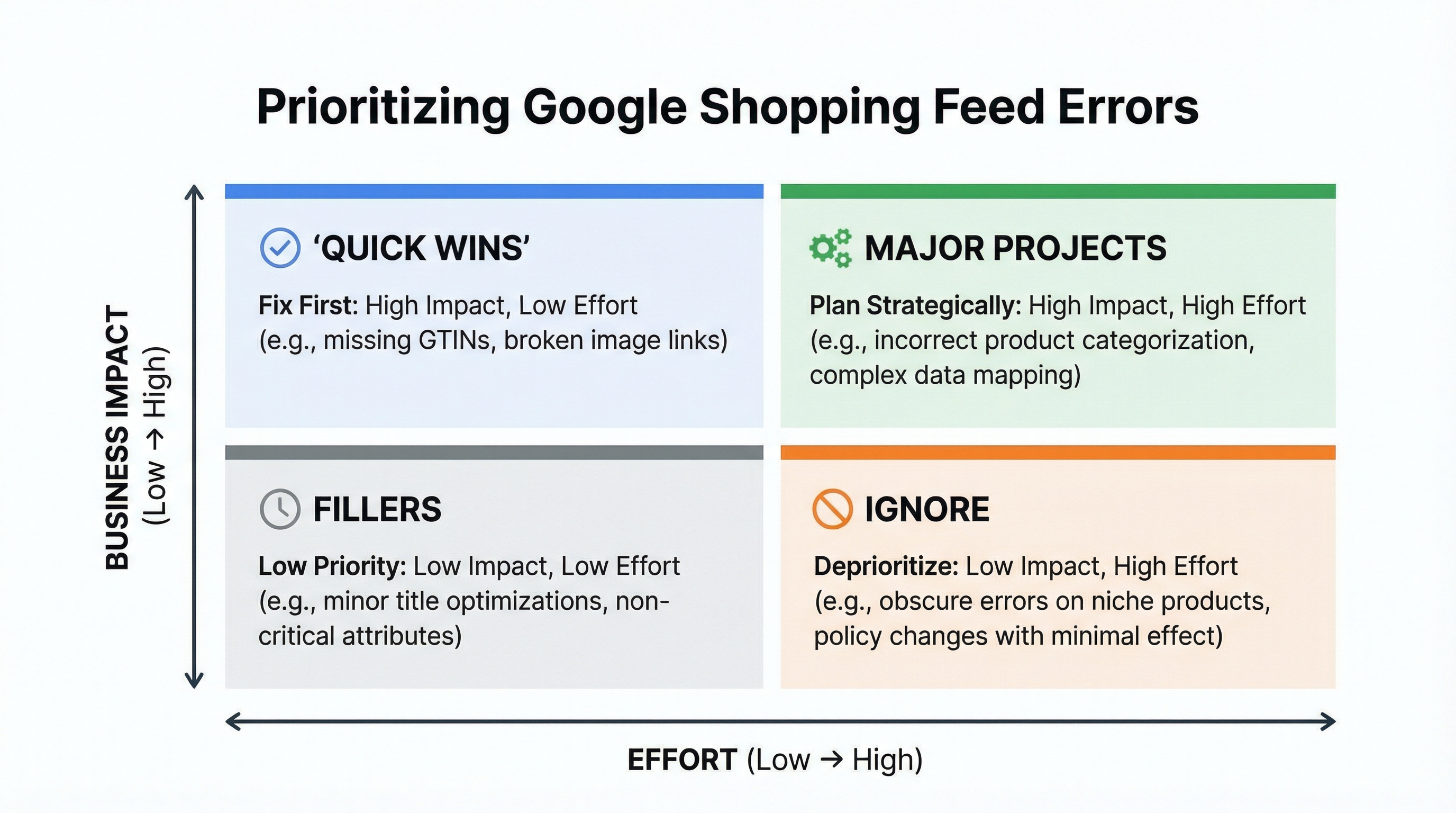
The panel centralizes errors and warnings that affect product visibility. Read the summary by type: account issues, feed issues, and item issues. An account issue can block entire campaigns; a feed issue usually affects entire batches; an item issue prevents specific SKUs from being published.
Example: If the diagnosis shows "missing price" on 2,000 products and "invalid URL" on 50, prioritize the missing price due to volume. Typical error: Fixing the most aesthetically visible flaw without quantifying its scope in lost sales.
Not all errors are worth the same for your ROAS. Calculate the estimated impact as the percentage of affected SKUs multiplied by their contribution to traffic or revenue. Estimated effort covers development time, PIM adjustments, or Shopify metafield mapping and validations.
Example: Fixing a global identification attribute for 100 products that generate 40% of sales is high impact and, typically, low effort if the data is already in the PIM. Typical error: Starting with cosmetic changes (yellow warnings) that do not increase impressions or unblock products.
The source of the error defines the scope of the correction:
Example: A policy suspension needs immediate attention and account unblocking before touching the feed. Typical error: Treating an account problem as if it were an attribute error and sending updates that do not unblock the account.
This is the minimum viable step-by-step for a QA that improves the feed without redoing the entire catalog:
Example: Correct title and GTIN in PIM, re-export, and confirm error reduction in 24-48 hours. Typical error: Re-exporting without validating the mappings between the PIM and the final feed.
Technical Note: The feed is the file that delivers product attributes to Merchant Center. The PIM is the master source of data. Shopify metafields are custom fields that allow mapping missing attributes. The Product Schema is the structured markup that helps catalog consistency (more info at Schema.org) and can influence feed quality. For official details, consult the Merchant Center Help Center.
In this section, we focus on the attributes that most impact visibility and rejection in a Google Shopping feed: GTIN, MPN, and Brand. The goal is to offer operational steps to detect inconsistencies and reduce rejections.
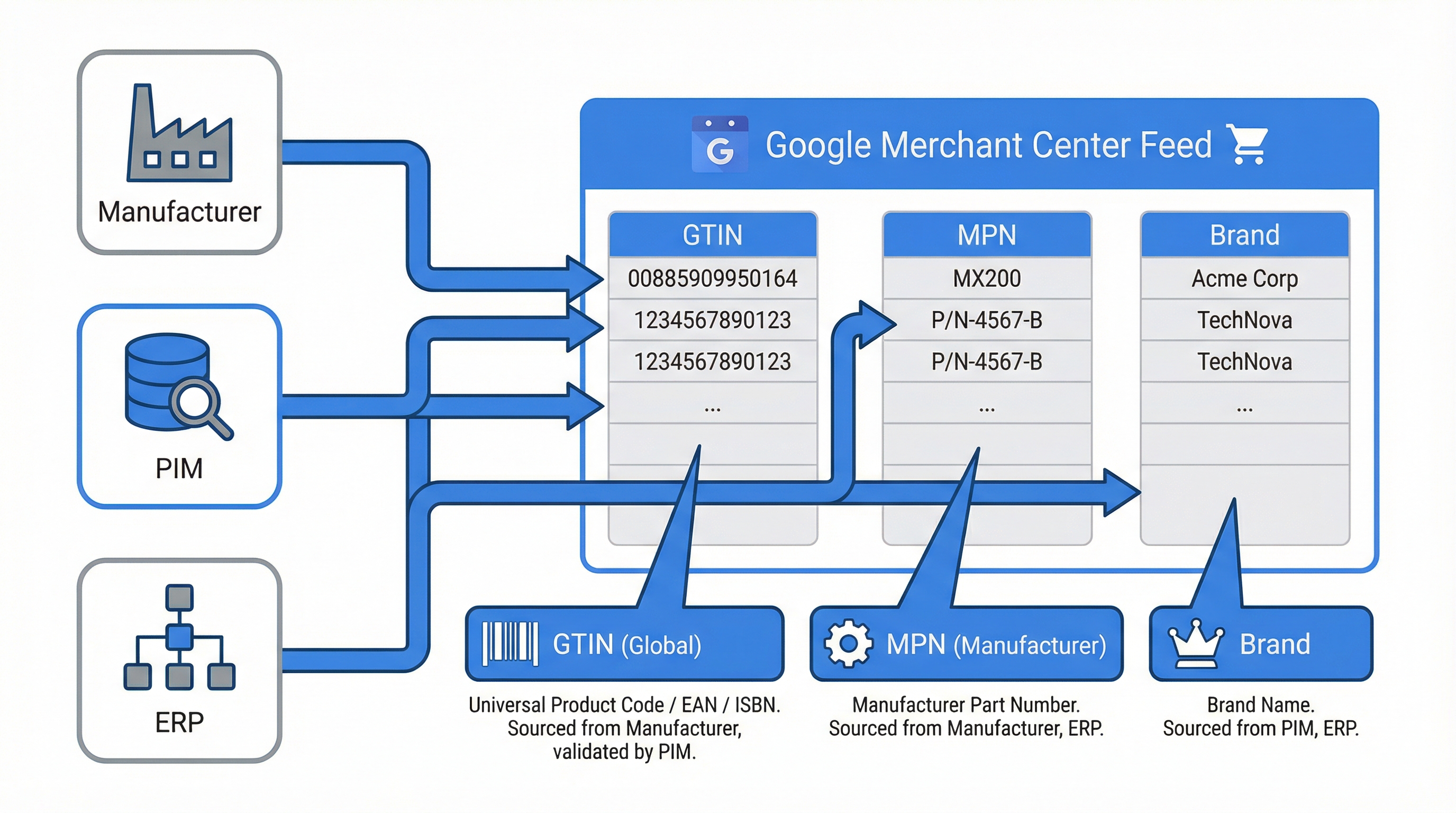
Unique identifiers allow Merchant Center to match your product with global inventory and Google rules, improving eligibility. Review Merchant Center reports to identify warnings related to identifiers and prioritize SKUs in campaigns with higher spend.
Example: Detect SKUs with a known brand but no identifier and group them by campaign priority. Typical error: Not reviewing Merchant Center warnings and assuming the feed is correct because there are no red rejections. Consult the official documentation on identifiers.
The GTIN is the global identifier preferred by Google and is usually mandatory when assigned by the manufacturer.
identifier_exists: no) and document the cause.The MPN helps identify variants and substitutes the GTIN when it is not publicly available.
REF-12345 normalized to 12345 using a text rule in the transformation.The brand is fundamental for eligibility and to avoid discrepancies that cause rejections for "missing information".
google_product_category and categorization coherenceGoogle's category affects tax rules and semantic matching.
Some products (handicrafts, white label) do not have GTIN or MPN and require special treatment.
identifier_exists as false for real cases and compensate with very detailed titles and descriptions, as well as attributes like color and size. Use Shopify metafields to store evidence.brand and mpn fields empty without marking identifier_exists: false, causing automatic rejections.Additional reading: Practical guide on EAN codes and catalog management.
This operational playbook allows you to correct and enrich your Google Shopping feed without redoing the entire catalog in the ERP. We will use supplemental feeds and feed rules to apply agile global changes.
Detecting rejection patterns and missing fields allows for immediate partial solutions. Export the error list from Merchant Center and group by rejected attribute.
Example: The list shows 120 SKUs with empty brand. You can create a supplemental feed that fills the brand from a metafield or apply a rule in Merchant Center that puts a default value ("General") if it is empty. Typical error: Applying manual corrections one by one without validating if a rule ("If brand is empty, use X") could solve it in bulk.
Supplemental feeds allow quick intervention in Merchant Center without touching the data source (Shopify/PIM) or integration pipelines.
id (mandatory) and the attributes to overwrite (e.g., custom_label_0). Upload as a supplemental feed and test with a subset.id, brand, custom_label_0 where 200 SKUs are updated for a sales campaign.Metafields allow adding commercial or technical information that does not exist by default in the Shopify product schema.
short_title, material, or recommended_use. Map those metafields to the feed export.short_title and map it with a feed rule to replace the main title when short_title is filled (useful for variants).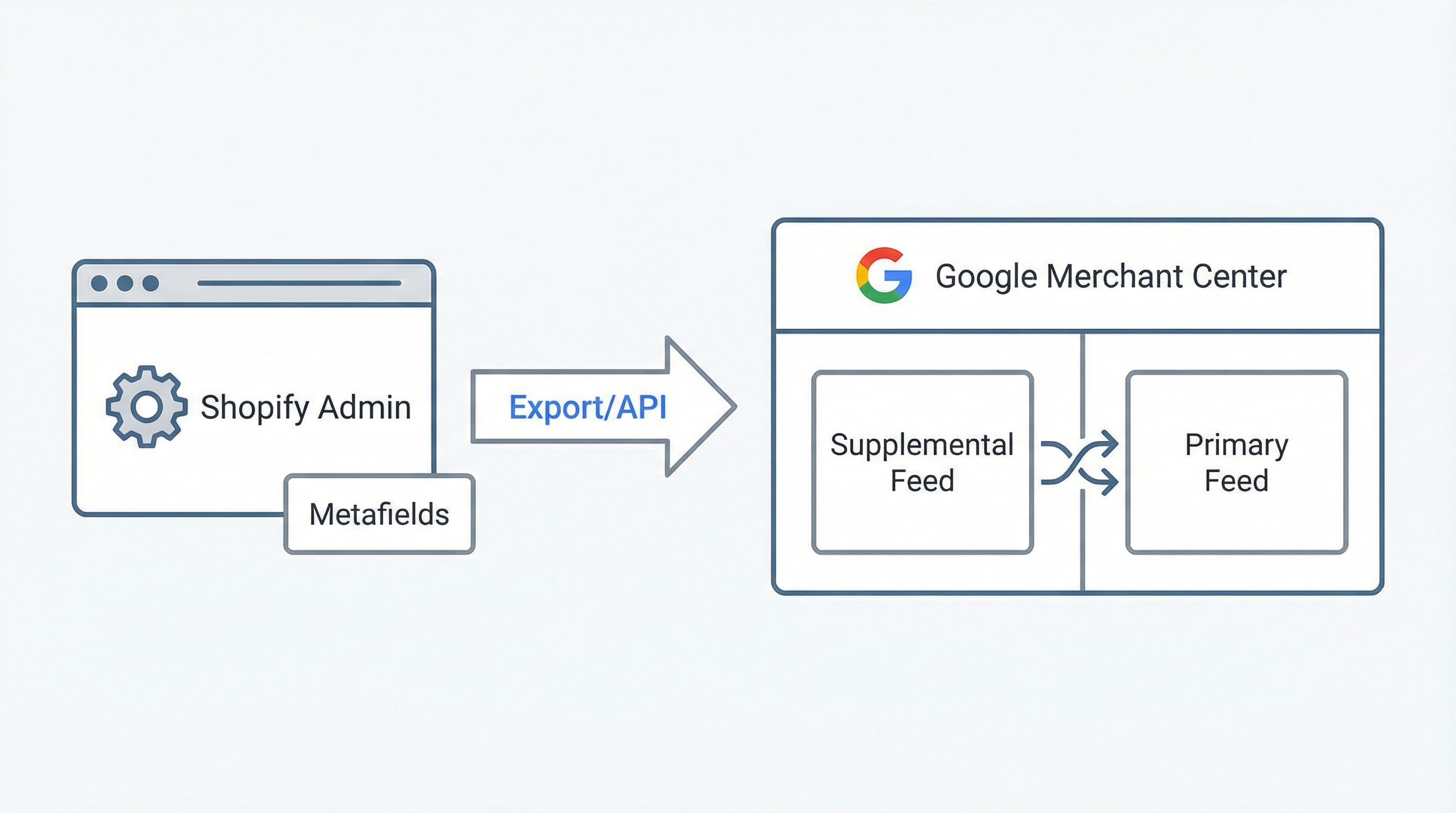
Titles and descriptions influence ad quality and CTR (Click Through Rate).
Create a simple matrix with impact vs. effort axis.
brand, color, or gender massively.A continuous QA routine reduces rejections and improves ROAS. Establish operational alerts and quality sampling.
Alerts reduce mean time to repair (MTTR) and prevent ad spend on products with erroneous data.
Sampling allows identifying patterns without reviewing 50k reference catalogs line by line.
Conduct weekly post-action reviews. Document solutions in an internal repository to avoid recurrence. Always use the Merchant Center data quality report as the source of truth.
Manual maintenance of attributes, GTINs, and descriptions at scale is usually unmanageable for small teams. ButterflAI automatically detects inconsistencies in the catalog, generates SEO-optimized metafields, and ensures your Google Shopping feed has the data density needed to maximize performance.
Quick answers to common questions.

Master your product data model, centralize attributes, and eliminate CSV chaos with an effective eCommerce PIM strategy.
Jan 27, 2026
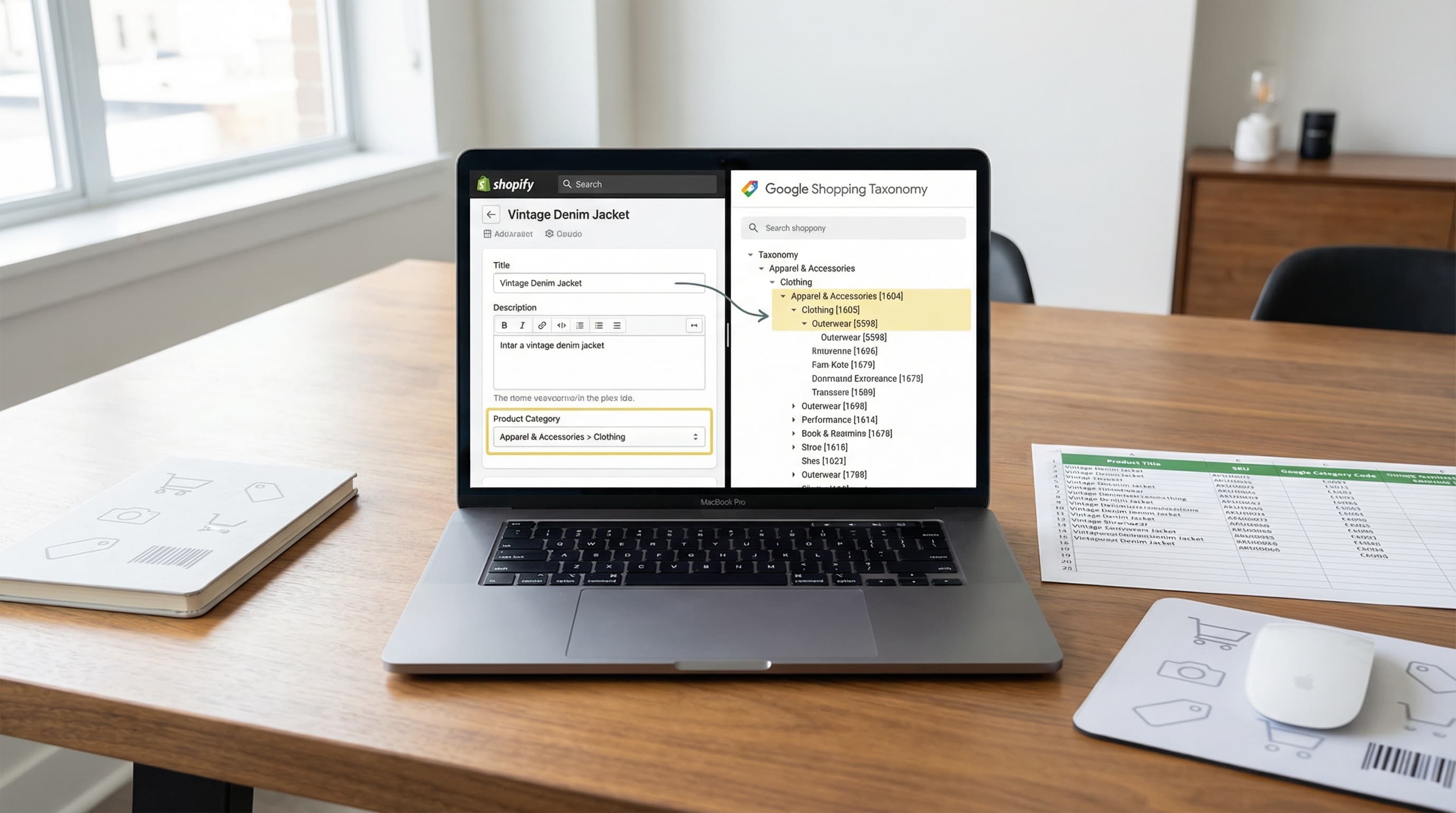
Master Google Shopping taxonomy to avoid Merchant Center disapprovals and improve campaign relevance.
Jan 26, 2026
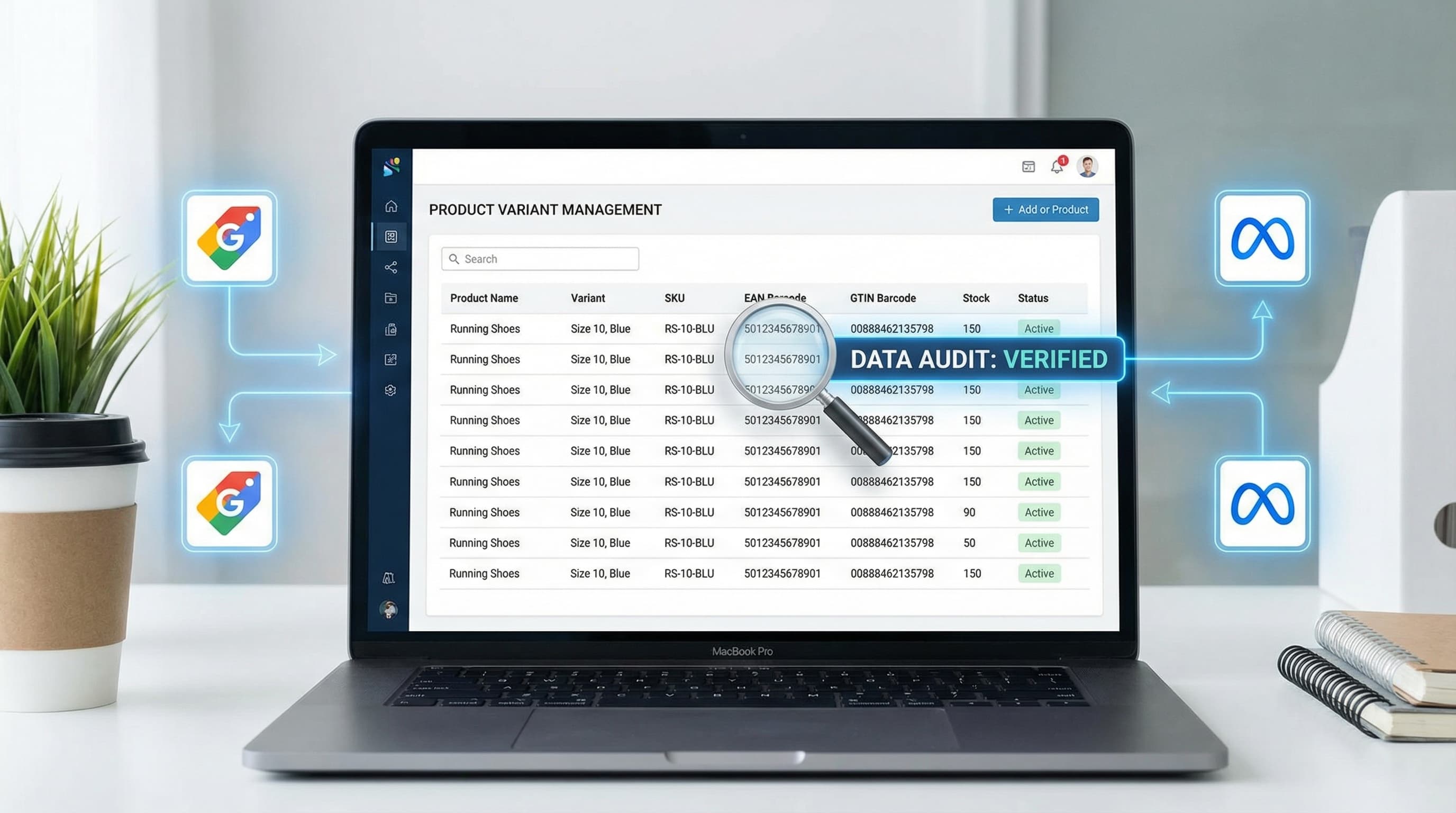
Learn how to manage product EAN codes to avoid Google Merchant Center errors and scale your omnichannel sales.
Jan 25, 2026