
How to Measure Product Data Quality: Ecommerce Scorecard
Discover how to measure data quality in your ecommerce catalog using the 6 core dimensions, channel-specific scorecards, and continuous remediation loops.
Feb 26, 2026
Master the Google Merchant Center feed: a guide to mapping variants, Shopify metafields, and identifiers to maximize visibility.
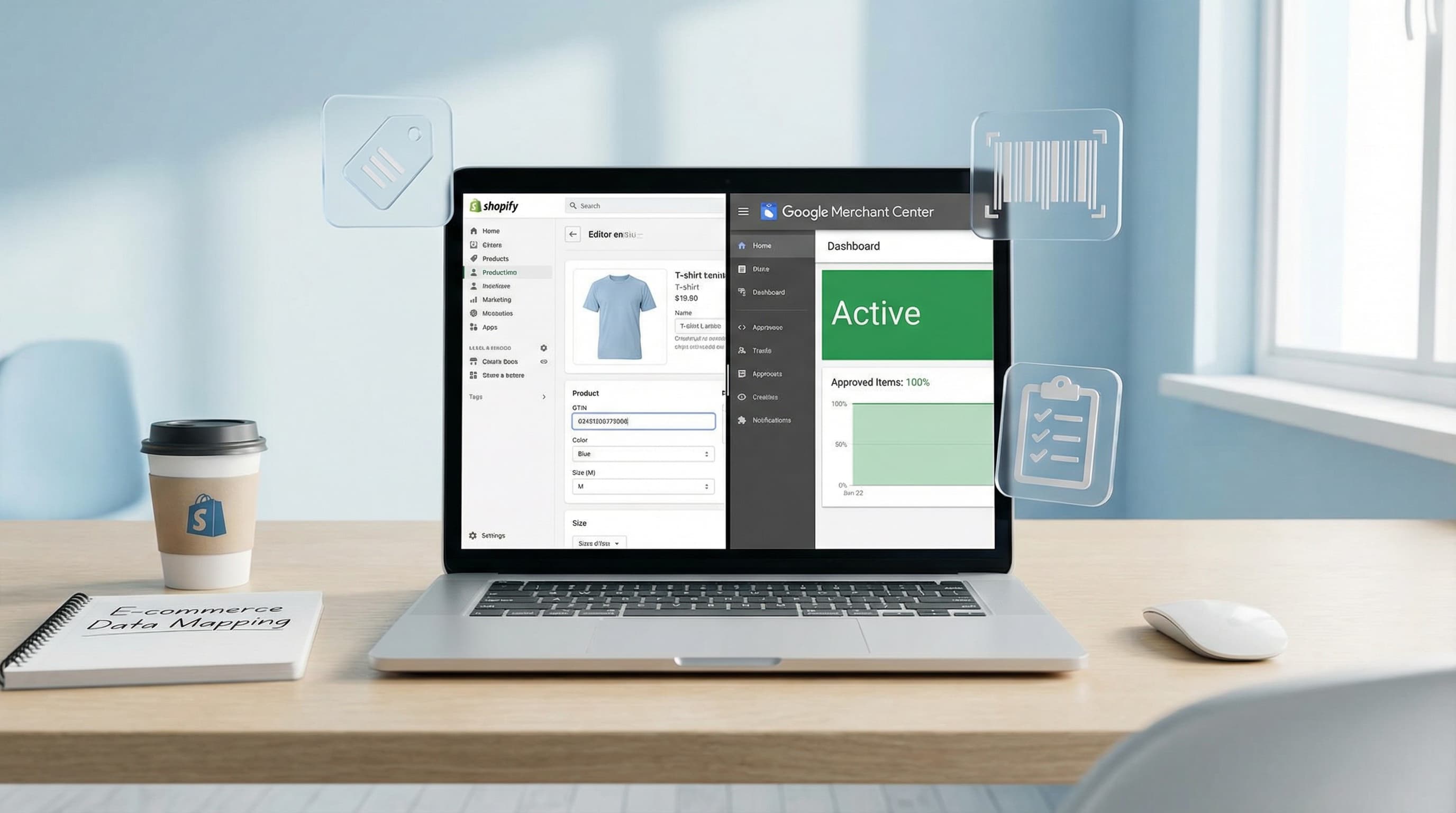
This text explains the Google Shopping attributes that truly matter to avoid rejections in Merchant Center and improve performance in Shopping and Performance Max campaigns. It includes a list of mandatory and recommended attributes, differences between identifiers and enrichment attributes, and a quality control checklist applicable in Shopify using products, variants, and metafields.
The most common rejections come from missing or inconsistent identifiers, prices or availability that do not match the store, and disallowed categories or images. Avoiding this requires mapping SKU, GTIN, brand, size, and color to Google attributes and maintaining data quality in the feed.
This is key because without these fields, the product may be rejected.
Common mandatory attributes: id, title, description, link, image_link, availability, price, shipping or shipping_label if applicable. For products with global identifiers, Google requires GTIN when applicable, and requests brand and MPN when there is no GTIN. Consult the official specification in Google Merchant Center Help.
Brief Example:
Map internal SKU to id, use a clean title, price with currency, and updated availability.
Typical Error: Sending prices different from those published in the store.
Understanding the difference helps prioritize data that prevents rejections versus data that improves performance.
Identifiers are GTIN, brand, MPN. Google uses identifiers to recognize the product in its global inventory and avoid duplicates. Enrichment attributes are size, color, material, product_type, google_product_category, and custom labels for campaigns.
Brief Example: If you sell sneakers, use GTIN and brand as identifiers and size and color as variant attributes.
Typical Error: Using the pack's GTIN instead of the sold unit's GTIN.
These attributes usually do not cause rejection but improve matching and performance.
product_type helps with internal organization. google_product_category improves relevance in Google Shopping. Custom labels facilitate segmentation in campaigns. For Performance Max, feed quality influences Google's ability to show the product in high-value conversions.
Brief Example:
Map Shopify collections to product_type and assign google_product_category according to Google's taxonomy.
Typical Error: Using overly general categories that reduce matching quality.
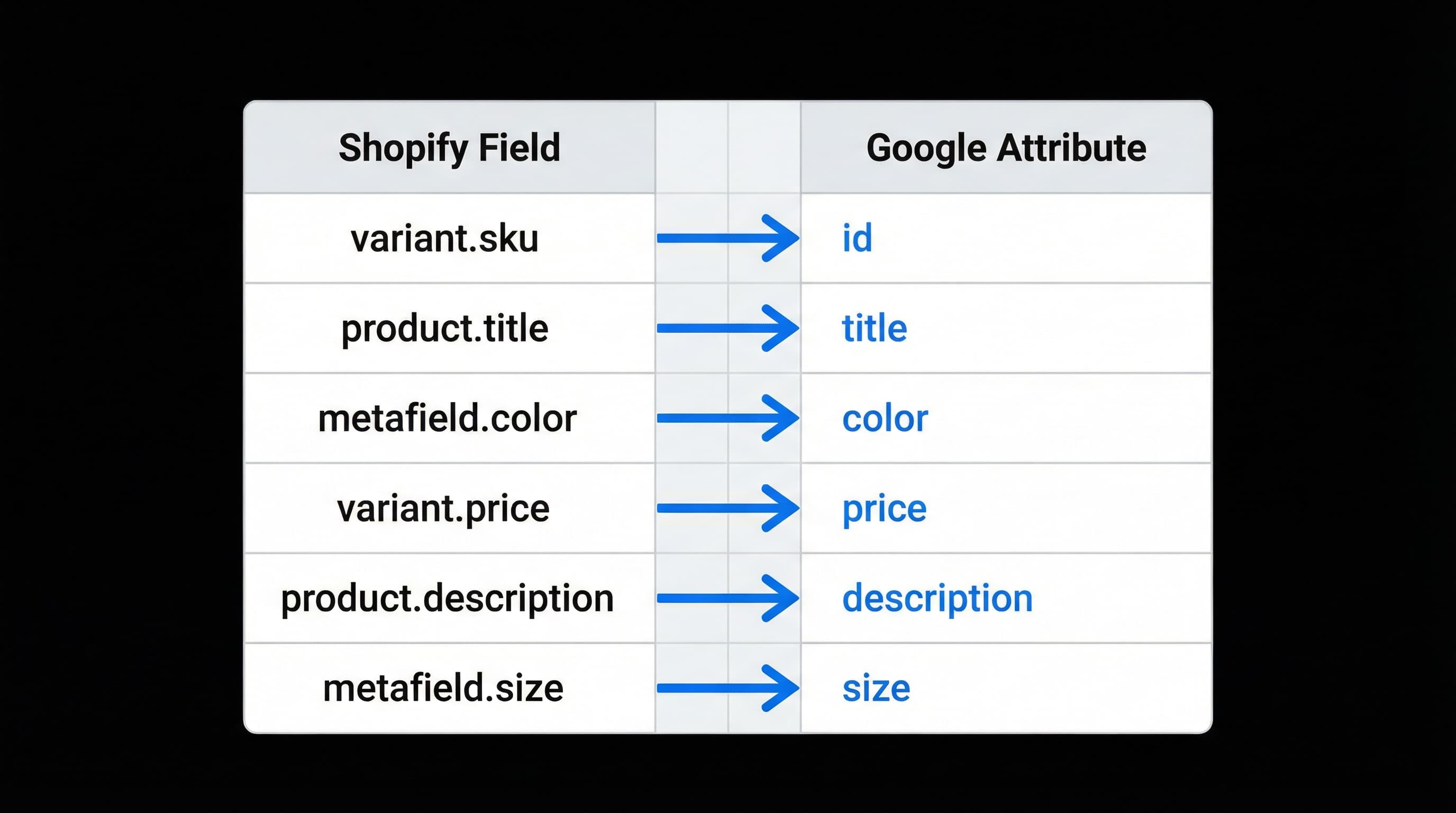
Better data quality reduces rejection, increases relevant impressions, and improves automated campaign learning.
Google uses attributes to understand the product and attribute conversions. Inconsistent data leads to automated disapprovals and visibility penalties. Maintaining synchronization between the store and the feed reduces errors.
Brief Example: A divergent price generates disapproval and a drop in impressions until corrected.
Typical Error: Not auditing the feed regularly and relying on a one-time sync.
What happens if I don't have a GTIN?
If no GTIN exists, use brand and MPN and add identifier_exists false if applicable. A typical error is marking identifier_exists true without valid identifiers.
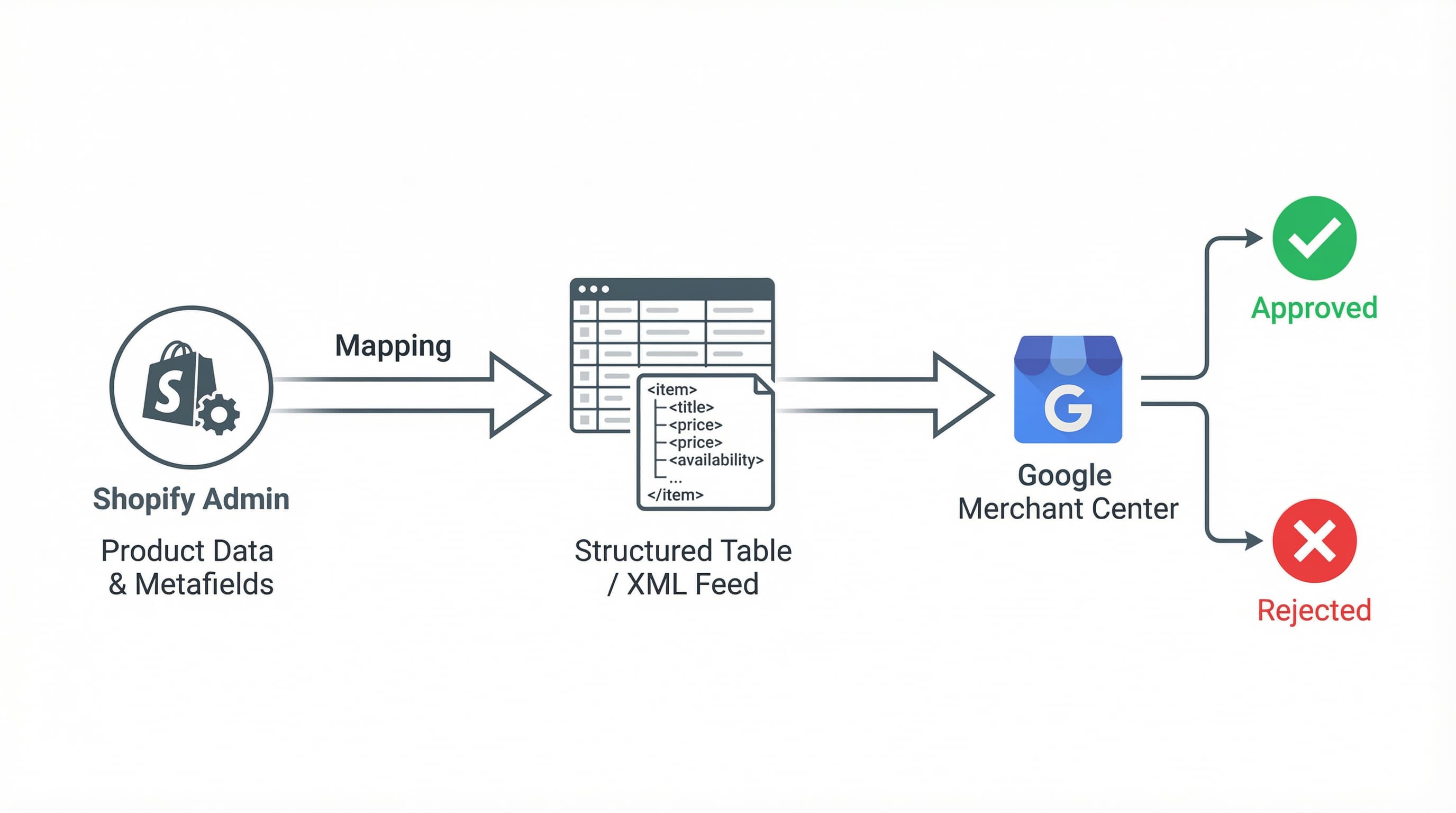
Mapping Google Shopping attributes from Shopify is an operational task that directly impacts feed delivery and visibility in Merchant Center. Below, we detail how to use Shopify products, variants, and metafields to cover information gaps and reduce rejections.
Prioritize identifiers, set rules by variant, and use variant-scoped metafields when the attribute changes between variants. Implement automated controls before sending the feed.
Context: Identifiers and variant attributes have the most impact on approvals and performance.
How to approach it:
identifier_exists false.product_type and google_product_category.Brief Example:
Send unique SKU per variant, variant.barcode when there is a GTIN, and variant.metafields.google.mpn for MPN.
Typical Error: Sending product-level data when variants differ.
Context: A metafield in Shopify is a custom field that stores additional product or variant data. It matters because it allows completing attributes that the native sheet does not cover and facilitates mapping by variant.
How to approach it:
Use a clear namespace like google and standardized keys. Prefer number types for numeric IDs and single line text for MPN.
Brief Example:
Namespace google, key google_mpn, type single line text in variant scope.
Typical Error: Saving variant data in product-level metafields.
Context: A standardized table speeds up feed development and reduces human error.
How to approach it: Adapt this table to your internal taxonomy and PIM if you use one. (Note: PIM is a central catalog management system that facilitates synchronizing data between channels).
| Merchant Center Attribute | Source in Shopify | Type | Operational Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | variant.sku or product handle | unique key | Use variant SKU when it exists |
| title | product.title | text | Clean HTML and microformats |
| description | product.body html | text | Truncate and clean special characters |
| link | product URL | url | Canonical link to product or variant |
| image link | product image per variant | url | Prefer image per variant |
| availability | variant inventory | enum | Sync real-time stock |
| price | variant price | number and currency | Include taxes if applicable by country |
| brand | product.vendor | text | Important for relevance |
| gtin | variant.barcode | text | Validate EAN-13 or UPC format |
| mpn | variant.metafields.google.mpn | text | Use metafield if no native MPN |
| identifier exists | computed | boolean | False for products without global identifiers |
| color | variant option or metafield | text | Normalize to short palette |
| size | variant option or metafield | text | Use standard format S M L or numbers |
| material | product.metafields.specs.material | text | Useful for advanced filters |
| product type | product.type | text | Map to google product category |
| google product category | product.metafields.google.category_id | number | Prefer using Google taxonomy ID |
Typical Error: Sending duplicate IDs in the feed.
Context: Metafields solve specific gaps when the store or PIM does not have all the necessary fields.
How to approach it:
Create namespace google and keys like google_gtin, google_mpn, google_category_id, google_identifier_exists. Use scoped metafields at the variant level for variable attributes. Maintain a master record of origin and transformation rules.
Brief Example:
variant.metafields.google.google_mpn configured with the manufacturer's MPN value.
Typical Error: Inconsistent names in keys that break automated mapping.
Context: Packs and bundles often fail if not treated as independent SKUs.
How to approach it:
Create a unique SKU in Shopify for the pack or manage the pack from the PIM with its own set of metafields. If the pack does not have a GTIN, mark identifier_exists false and provide MPN or brand when possible. Show price per unit when the marketplace allows it.
Brief Example:
Product "Pack 3x Towel" with SKU PACK_TOW_3 and metafield google_identifier_exists false.
Typical Error: Sending a pack as a collection of variants without a unique SKU.
Google Shopping attributes are the foundation for your products to appear correctly in results and ads and to reduce rejections in Merchant Center. This operational checklist is designed for eCommerce teams using Shopify and PIM. It includes an initial audit, format validations, and a 90-day roadmap to keep the feed healthy and optimize ROAS.
Why it matters: Without a field inventory, you don't know the real quality of the catalog.
How to approach it: Export a CSV of products and variants from Shopify and extract a file of the current feed. Compare SKU, barcode, gtin, brand, color, size, product_type, and any metafield columns. Prioritize top SKUs by sales and SKUs with frequent errors in Merchant Center.
Example: Simple table with columns SKU, variant id, gtin, metafield.color, and google_product_category.
Typical Error: Assuming all GTINs are in the Shopify barcode field.
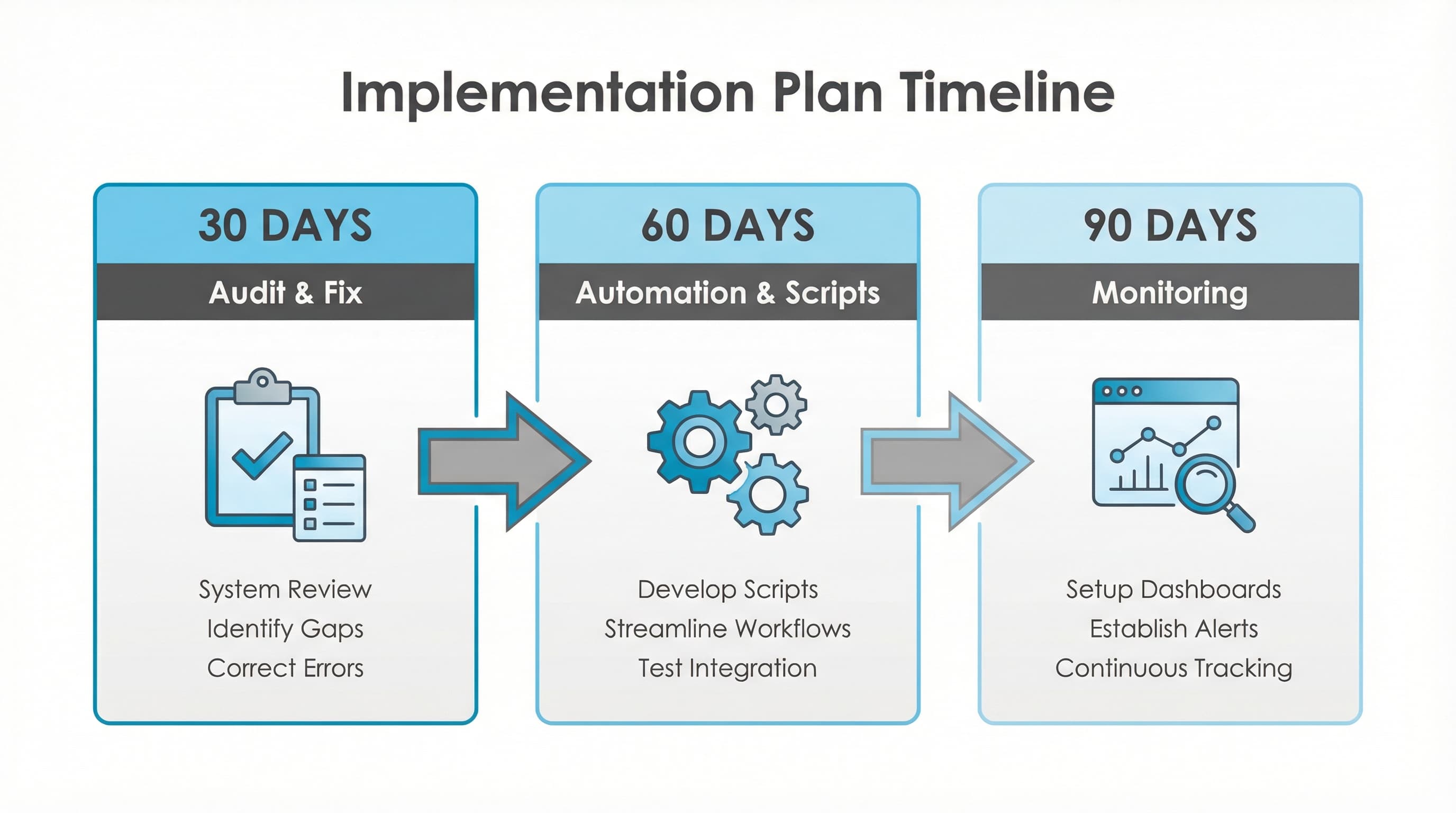
Why it matters: Many Merchant Center rejections are due to incorrect format or disallowed values.
How to approach it: Define automated rules that validate GTIN by length and numbering (8, 12, 13, 14 digits), price with currency, availability with allowed values, and condition. Implement scripts or rules in your PIM or a validation app to flag and export errors.
Example: A rule that raises an alert if gtin contains letters or does not have standard length.
Typical Error: Validating GTIN only by length without checking for non-numeric characters.
Why it matters: Detecting rejections quickly avoids loss of impressions and inefficient spend.
How to approach it: Integrate daily checks that compare the generated feed with errors reported in Merchant Center. Prioritize corrections by impact on impressions and sales. Maintain basic KPIs: percentage accepted, number of critical rejections, and average time to correction.
Example: Weekly ticket flow to correct 20 SKUs with "missing gtin" error.
Typical Error: Reacting only when Google marks the rejection without analyzing the root cause.
Why it matters: Sequencing work avoids rework and improves sustained quality.
How to approach it: Divide into 30-day phases.
Operational Example: Week 1 map top 500 SKUs, week 5 deploy scripts, week 9 review KPIs and adjust priorities.
Typical Error: Trying to correct the entire catalog without prioritizing by impact.
google_product_category and product_type in metafields.Managing the attribute granularity required by Google Shopping (GTINs, variant metafields, specific categorization) often leads to manual errors and constant rejections in Merchant Center.
ButterflAI detects discrepancies in your catalog, automatically standardizes attributes, and ensures your Shopify variant information meets technical feed requirements before it affects your campaigns.
Go deeper with guides and tools connected to this topic.
Quick answers to common questions.

Discover how to measure data quality in your ecommerce catalog using the 6 core dimensions, channel-specific scorecards, and continuous remediation loops.
Feb 26, 2026
Stop guessing with basic Etsy SEO tips. Map your catalog data to Etsy attributes, automate descriptions, and scale your listing optimization strategy systematically.
Feb 25, 2026

Optimize your Pinterest feed with a field-by-field checklist and automated QA workflow. Scale Shoppable Pins and Pinterest Catalog Ads without the manual chaos.
Feb 24, 2026