
Google Shopping Feed Audit & Optimization: The Complete Guide
Learn to diagnose, prioritize, and fix product feed errors to improve ROAS for Shopping and Performance Max campaigns.
Jan 30, 2026
Master Google Shopping taxonomy to avoid Merchant Center disapprovals and improve campaign relevance.
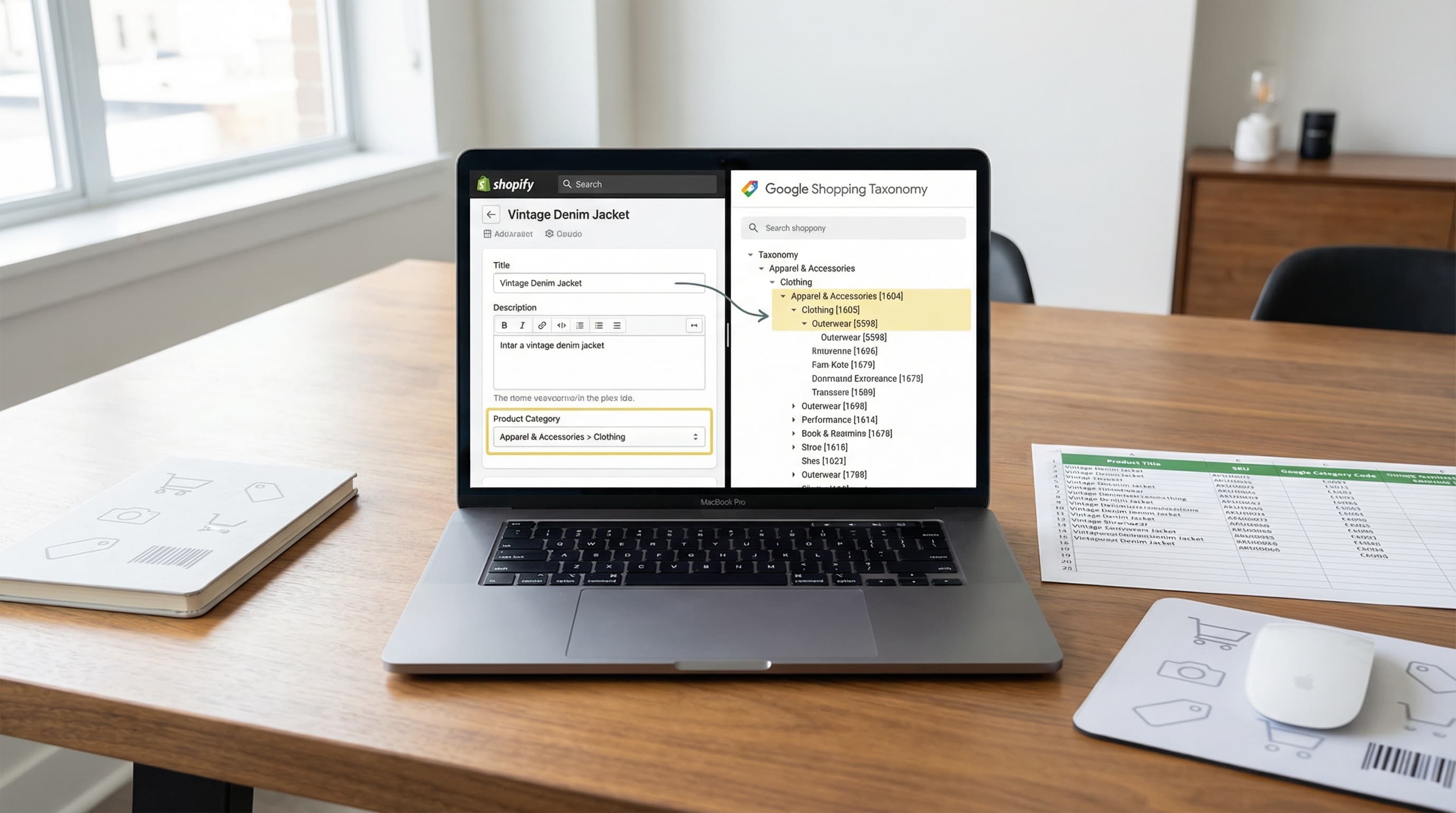
The Google Product Category (GPC) is the official taxonomy used by Google Shopping to classify products within its ecosystem. Unlike your store's internal organization, this standardized classification allows Google to understand exactly what you are selling, improving impression relevance and drastically reducing the risk of rejection due to policy non-compliance.
In the Shopify environment, it is fundamental to understand that the GPC is not the same as the "Product Type". While the Product Type is an internal classification for organizing collections and filters on your storefront, the GPC is a technical requirement for standardization in Merchant Center.
To manage this correctly, you need to master some technical terminology:
The most common mistake is sending Shopify's "Product Type" (e.g., "Cool T-Shirts") as if it were the Google category. This confuses the algorithm. Google uses the GPC to apply automated classification rules and specific policies (for example, attribute requirements for apparel or electronics).
To fix this, keep your Product Type for internal operations and map the GPC as a separate attribute. The best practice is to implement metafields in Shopify to store the numeric GPC ID and export it in the feed.
Practical Example:
- Incorrect: Sending "Running Shoes" (text) in the category field.
- Correct: Storing the metafield
gpc_id: 267(which corresponds toApparel & Accessories > Shoes) to ensure correct reading in Merchant Center.
A correct GPC improves the match between the user's search query and your product. This translates to higher quality traffic and often an increase in CTR. Additionally, certain Merchant Center policies are triggered by category; poor classification can trigger warnings or automatic disapprovals (for example, if you classify a health product as "Home", you will be asked for attributes you don't have).
To mitigate risks, audit your priority categories by comparing them against the official taxonomy list and specific guides for sensitive verticals like fashion or cosmetics.
Choosing the appropriate depth in the taxonomy directly affects approvals in Merchant Center and the performance of Shopping campaigns (PMax). The goal is to balance specificity with operational coverage.
It is not always necessary to reach the leaf level of the taxonomy. The general rule is: prioritize the most precise category that describes the product without generating "false negatives" (erroneous classifications due to being too specific).
Step 1: Identify the Feed Objective The use of the feed determines the granularity.
Women's Running Shoes should map to a subcategory that includes sport and gender if it exists.Typical Error: Using root categories (e.g., "Apparel") for the entire catalog, losing relevance in "long-tail" searches.
To scale, you need consistent rules that reduce ambiguity and allow mapping automation from a PIM or via feed rules.
Create "If... Then" rules based on PDP (Product Detail Page) attributes such as material, usage, gender, or brand.
Example of Decision Logic:
Vehicles > Bicycles.Mountain Bikes (specific ID).Bicycles.Document and version these rules. If multiple attributes point to a subcategory, select the deepest one; if data is missing, be conservative and go up a level.
Quick audits reduce "Disapproved" time in Merchant Center.
google_product_category or a default value.Manual management in the Shopify admin is unfeasible for large catalogs. The strategy must be based on structured data (Metafields) and bulk edits (CSV).
Metafields are the safest way to maintain feed data in Shopify without "cluttering" the description or tags.
Recommended Configuration:
feed_datagoogle_product_category_idInteger (Whole number)Technical Note: Store the numeric ID (e.g.,
187), not the text path. Text is prone to typos ("Apparel" vs "Aparel") that break the feed. The ID is unequivocal.
Decide if the category applies at the Product or Variant level. In verticals like Fashion, it is often necessary to go down to the variant level if, for example, you sell equipment that changes category based on size or gender (e.g., children's clothing vs. adult may have different IDs).
For catalogs exceeding hundreds of SKUs, use Shopify's import/export or data management apps (like Matrixify).
Handle and the defined metafields.VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP) to cross-reference your internal "Product Types" with a master table of Google IDs.Changes in Google's taxonomy or your own inventory can misalign data. Establish a monthly process.
SKU | GPC ID | Merchant Center Status.Operational Maintenance Checklist:
Mapping thousands of references against a taxonomy that changes annually is an operational time sink and a common point of failure in Shopping strategies. Silent category errors may be costing you quality impressions without generating an explicit "rejection".
ButterflAI addresses this problem by semantically analyzing your catalog to assign the most precise Google Product Category at scale.
ButterflAI detects discrepancies between your title, description, and the assigned category, suggesting the correct numeric ID and automatically updating the corresponding metafield in Shopify. This ensures your feed always goes out with the maximum possible granularity, improving ad relevance and reducing manual spreadsheet maintenance work.
Quick answers to common questions.

Learn to diagnose, prioritize, and fix product feed errors to improve ROAS for Shopping and Performance Max campaigns.
Jan 30, 2026
Master your product data model, centralize attributes, and eliminate CSV chaos with an effective eCommerce PIM strategy.
Jan 27, 2026
Learn how to manage product EAN codes to avoid Google Merchant Center errors and scale your omnichannel sales.
Jan 25, 2026