
Google Shopping Feed Audit & Optimization: The Complete Guide
Learn to diagnose, prioritize, and fix product feed errors to improve ROAS for Shopping and Performance Max campaigns.
Jan 30, 2026
Learn how to manage product EAN codes to avoid Google Merchant Center errors and scale your omnichannel sales.
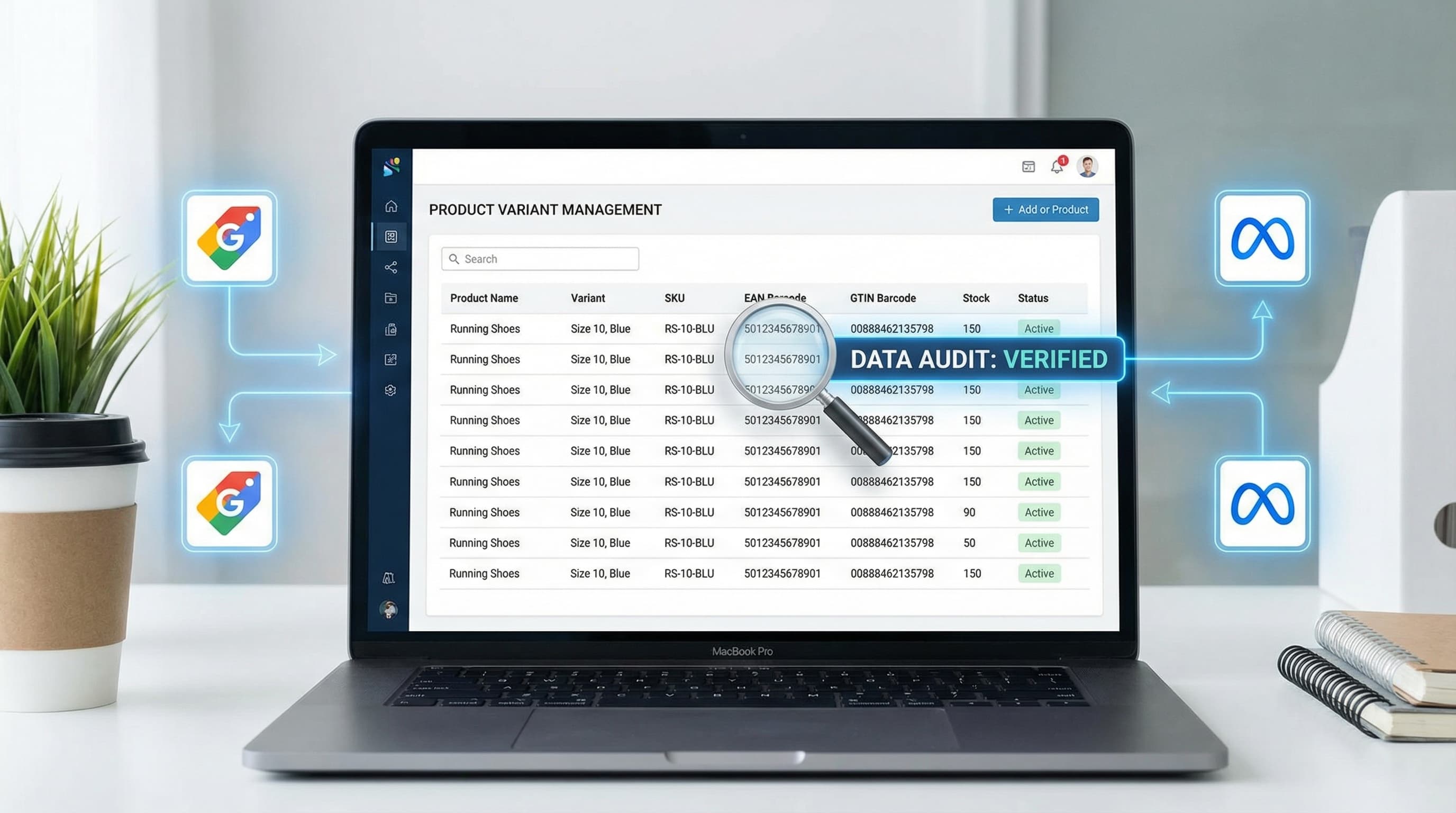
The EAN code is the most common physical identifier in European retail and forms the technical basis for most catalog quality rules in a digital environment. However, terminological confusion between EAN, GTIN, UPC, and MPN is the root cause of thousands of synchronization errors in data feeds.
In this section, we clarify the technical hierarchy, critical differences with other identifiers, and why channels like Google Merchant Center demand absolute precision to avoid product suspensions.
To avoid mapping errors and ownership conflicts between sales channels, it is vital to distinguish between the standard, the format, and the manufacturer reference.
GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) is the umbrella term for global product identifiers standardized by the GS1 organization. It is the abstract concept that encompasses the physical formats we see in barcodes:
On the other hand, the MPN (Manufacturer Part Number) is the internal reference assigned by the manufacturer. Unlike the GTIN, the MPN does not guarantee global uniqueness (two different manufacturers could use the reference "A-100").
How to approach it in your catalog:
Always validate the length and the checksum (check digit) before accepting a code into your database. A headphone set with a 13-digit code is an EAN (GTIN-13). A book must map to the isbn field in the feed. Never use the MPN in the GTIN field; this is a critical error that confuses product matching algorithms on marketplaces.
Source: Official information on standards at GS1.
Google uses the GTIN to group offers for the same product sold by different retailers. Knowing their exact policy prevents mass rejections and the loss of impressions in Shopping.
Google makes GTIN mandatory when the product has a manufacturer-assigned GTIN and the feed provides the brand. If the product is a craft, custom-made, or an antique without a code, Google allows omitting it using the identifier_exists attribute (which we will cover later), but requires proof.
Impact Example: A recognized brand smartphone (e.g., Samsung Galaxy) listed without its GTIN will be immediately flagged as "Insufficient product information" and will lose eligibility to appear in Shopping ads, regardless of your bid.
Typical Error:
Uploading feeds that include the brand and the mpn, but leave the gtin field empty when the product actually exists in the GS1 catalog. This triggers a "Missing GTIN" alert.
Source: Official policy on identifiers in Google Merchant Center.
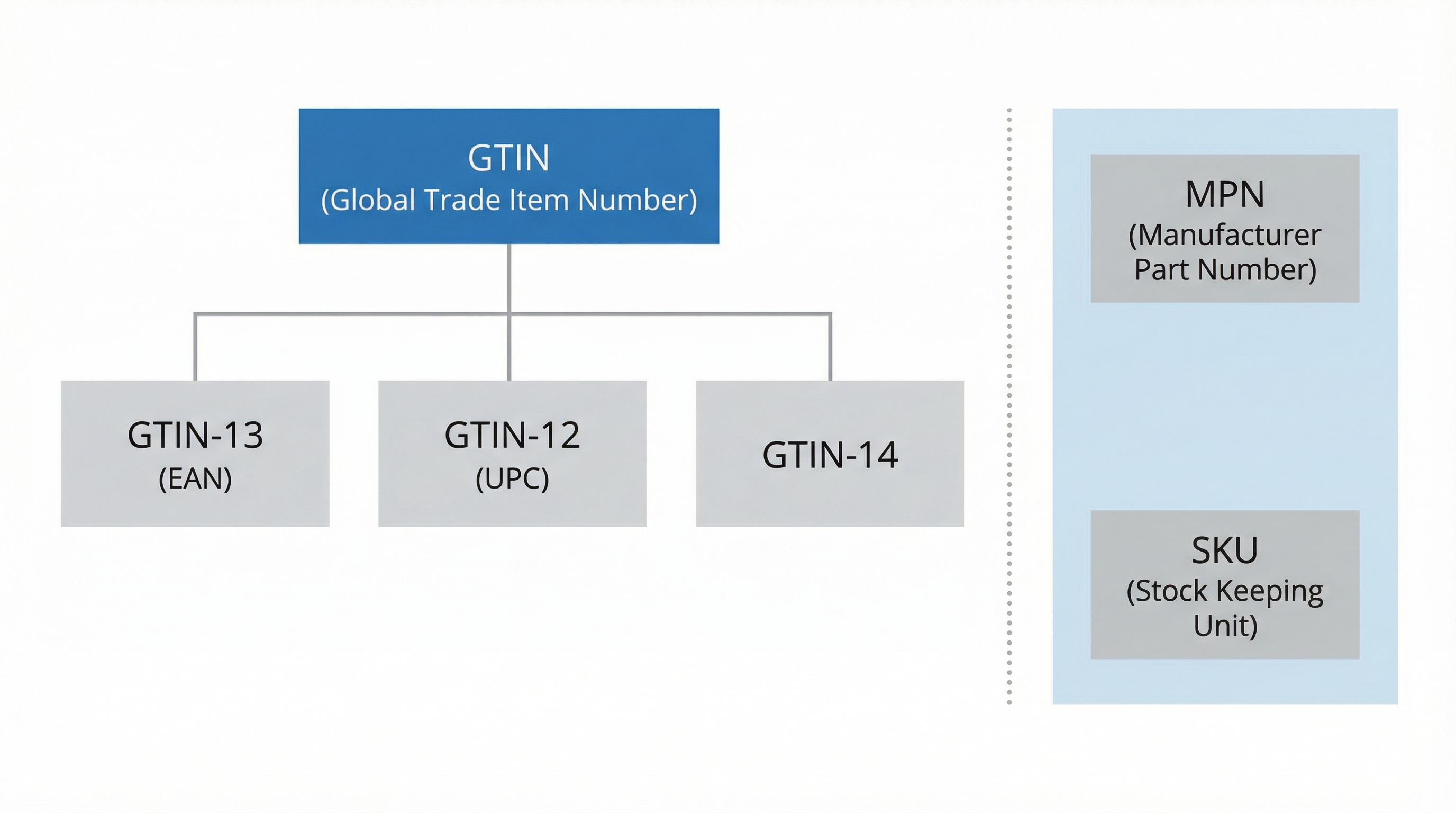
To reduce discrepancies between your e-commerce and marketing channels, you need a master field (Source of Truth) at the variant level, not the parent product level.
Storage Strategy:
gtin field for each variant. The PIM acts as a centralized system that feeds both Shopify and marketing feeds, ensuring the data is identical everywhere.gtin and mpn. Metafields are custom fields that allow storing additional structured attributes, making it easier for feed apps and ERPs to read the correct data without having to "scan" the description or title.Implementation Example:
Create a gtin_text text attribute per variant in the PIM. Map it in the integration to populate the shopify.metafields.product.gtin metafield. Upon export, the feed will read this metafield.
Source: Guide to managing identifiers in Shopify.
A feed is the file (XML, CSV) or API that sends your products to external channels. Clear mapping rules at this stage prevent automatic errors.
Recommended Transformation Logic:
In your export pipeline (feed management tool), always prioritize the gtin field coming from the PIM/Metafield. Implement a "fallback" rule:
gtin is not empty → Use gtin.gtin is empty AND mpn exists → Use mpn and mark identifier_exists = false (if applicable according to the category).Transformation Pseudorule:
IF gtin IS NOT EMPTY THEN map_to 'gtin' ELSE IF mpn IS NOT EMPTY THEN map_to 'mpn' AND set 'identifier_exists' to 'false'.
Typical Error:
Sending "dirty" GTINs (e.g., 123-456-789) which cause the total rejection of the item in the feed due to invalid format.
The EAN Code is critical not only for Google but for maintaining operational coherence between your store, your ERP, and marketplaces (Amazon, Zalando, etc.). Here we delve into governance: how to obtain them, how to decide their inheritance, and how to structure the data.
Without a documented policy, every department (purchasing, logistics, marketing) will apply different criteria. This guarantees duplicates.
The Minimum Viable Policy: Document when it is mandatory to use a GS1 GTIN and when an internal identifier is allowed.
local_only to exclude them from GTIN requirements in feeds.Resource: GS1 is the only authorized source for generating interoperable codes. Consult their standards at GS1 Standards.
The decision to apply the EAN to the "parent" product or to the "child" variants is the source of greatest friction in fashion catalogs and complex variants.
Decision Framework:
Inheritance Logic in Export:
Configure your feed to look for the value in this order: Variant > Product. If the variant has a GTIN, use it. If not, check if the parent product has one (only valid for simple products).
Typical Error: Using the same GTIN for all sizes of a t-shirt. Google will detect that the same identifier points to different SKUs and will reject all of them for "Duplicate GTIN".
Advanced marketplaces may audit the ownership of the GTIN prefix.
Obtaining Process: Buy blocks of GTINs directly from GS1 for the countries where you operate. Avoid resellers of cheap codes, as they often belong to other companies and will generate brand conflicts on Amazon or Google.
gtin_source, date_assigned, and validation_status.A multipack is a sales unit distinct from its components.
How to Manage It: Assign a unique GTIN to the pack. In the PIM, create a "contains" relationship linking the pack SKU with the quantity of the base SKU.
multipack attribute as true (or indicate the quantity) and export the pack's GTIN.Even with good policies, data degrades. This section covers how to audit your catalog massively before critical dates (Black Friday, Sales) to ensure no "top seller" is rejected due to EAN problems.
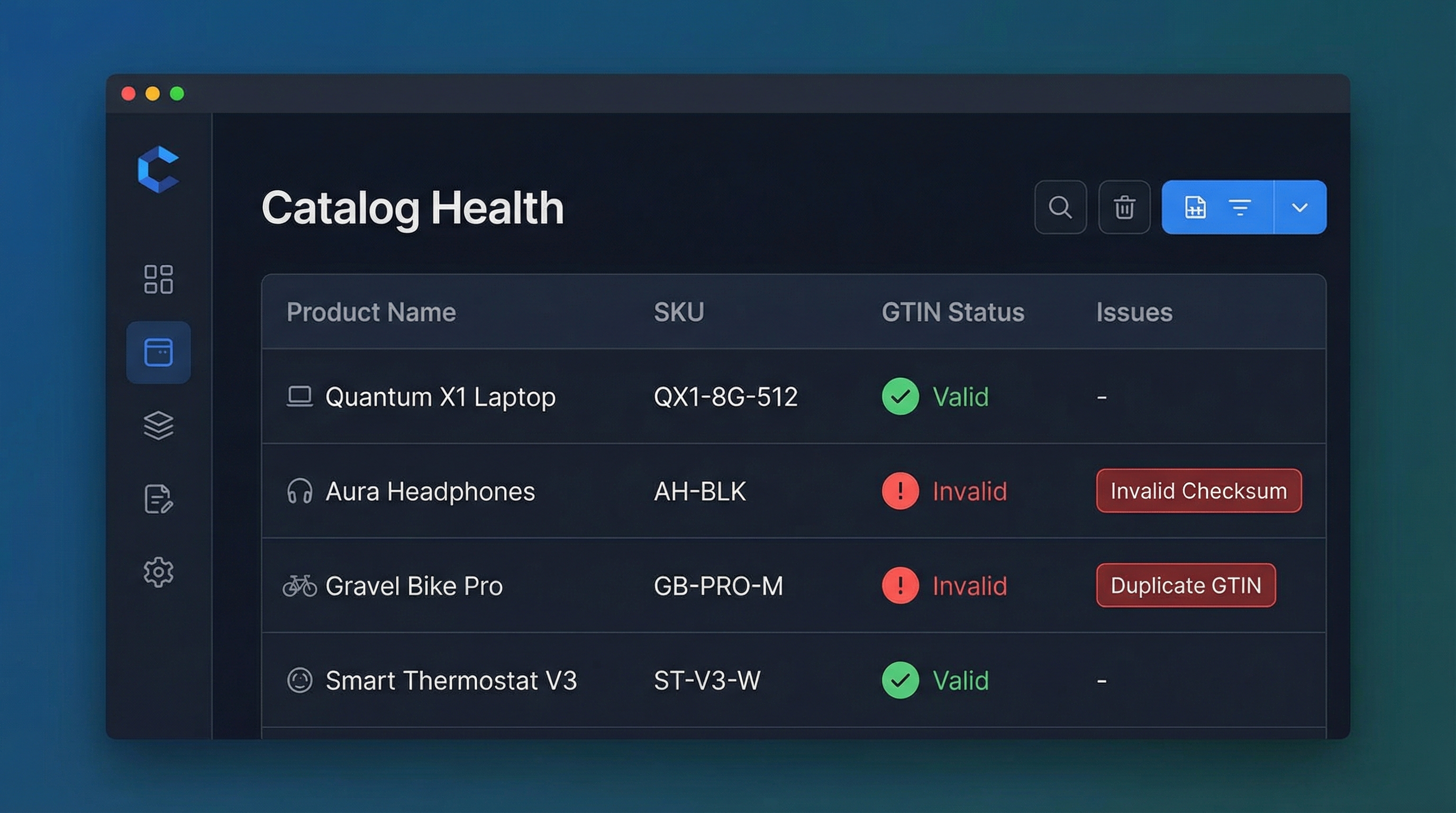
Incorrect codes generate silent rejections: the product uploads, but receives no impressions.
Batch Validation Strategy:
Extract a complete dump of your catalog (CSV/Excel) with the columns: sku, variant_id, gtin, mpn, and identifier_exists. Run a script or use formulas to validate:
Produce a report with three columns: status (Valid/Invalid), reason (Incorrect Checksum/Wrong Length), and action (Correct in PIM).
Typical Error: Applying manual corrections in the feed (for example, adding a leading 0 to convert UPC to EAN) without correcting the data in the PIM, which perpetuates the error in future synchronizations.
identifier_exists AttributeGoogle and Meta allow products without GTIN, but only if you use this attribute correctly. Misuse (marking everything as false to avoid looking up codes) can lead to account suspension.
Assignment Logic:
gtin is present and valid → Export gtin.gtin is empty AND the product is "custom" (craft, private label without GTIN, antique) → Export identifier_exists = false.More Info: Consult the product data specification from Google and the catalog documentation from Meta.
Follow this protocol before connecting a new feed or after a massive catalog update:
gtin fields pass the length and checksum test?shopify.metafields.namespace.key and not the description?Maintaining EAN/GTIN identifier integrity manually across thousands of SKUs is a task prone to human error and consumes hours of technical management.
ButterflAI audits your catalog in real-time, detecting inconsistencies in identifiers, validating checksums, and ensuring the variant structure meets strict Google Merchant Center and Meta requirements. The platform allows for massive correction of these attributes and generates optimized descriptions and metadata, guaranteeing your products are not only approved but also positioned better.
Quick answers to common questions.

Learn to diagnose, prioritize, and fix product feed errors to improve ROAS for Shopping and Performance Max campaigns.
Jan 30, 2026
Master your product data model, centralize attributes, and eliminate CSV chaos with an effective eCommerce PIM strategy.
Jan 27, 2026
Master Google Shopping taxonomy to avoid Merchant Center disapprovals and improve campaign relevance.
Jan 26, 2026