How to Scale FAQ Schema Markup on Product Pages
Discover a governance-first workflow to create high-intent product FAQs from real customer data, deploy safely, and measure SERP CTR impact.
Feb 20, 2026
Technical guide to optimize crawl budget, control filters, and avoid duplicate content in Shopify catalogs.
Robots.txt in Shopify sets the first barrier for search engine crawling of routes but does not by itself determine which pages are indexed. Understanding the difference between crawling and indexing, and their relationship with sitemaps and rel canonical, prevents changes that reduce the visibility of large catalogs.
Context: Crawling is the request a bot makes to retrieve a URL; indexing is the search engine's decision to store and display that page.
Approach: Use robots.txt to limit the routes that can be requested by bots, and use noindex tags or rel canonical to control what gets incorporated into the index. Robots.txt prevents a bot from downloading the content but does not prevent the URL from being known if external links exist. For technical reference consult Google Search robots docs
Brief example: A page blocked in robots.txt may appear as a known URL in Search Console even if it is not indexed.
Typical error: Confusing blocking with applying noindex and cutting off access to CSS or JavaScript files necessary for rendering.
Context: robots.txt tells crawlers if they can request a URL; Shopify serves a dynamic robots.txt by default.
Approach: Use robots.txt to reduce crawling of administrative endpoints, unnecessary public APIs, and parameters that generate trivial variations. Do not block assets or sitemaps that facilitate rendering and discovery. robots.txt.liquid is the theme template that allows customizing rules in stores that support it and is critical because an error can prevent Google from loading resources.
Brief example: Blocking filter parameters reduces requests on collections while keeping the canonical version of the catalog indexable.
Typical error: Blocking feeds or sitemaps by accident and cutting off the main discovery channel.
Context: Not all stores allow the same level of customization and some rules are managed by the platform.
Approach: If you edit robots.txt.liquid, test changes in a staging environment and validate with Search Console that JSON, CSS files, or endpoints used by the storefront are not blocked. Combine selective blocking with canonical and noindex to resolve duplicates and low-quality pages.
Brief example: A broad rule blocking /assets/ prevents script execution and degrades page evaluation.
Typical error: Applying a generic template without adapting theme routes and breaking rendering.
Context: Validation prevents a change from impacting indexing without warning.
Approach: Use URL inspection and the coverage report in Google Search Console to check access and indexing. After updating robots.txt, request re-inspection of the affected URLs.
Brief example: A URL marked as blocked by robots.txt should become accessible after updating the file and requesting re-inspection.
Typical error: Not requesting re-inspection and assuming Google will re-evaluate immediately.
Conclusion
Robots.txt controls access to crawling but not final indexing. In Shopify, combine robots.txt, sitemap, and rel canonical to reduce crawl waste and protect catalog visibility.
Editing robots.txt in Shopify without breaking indexing is a necessity for stores with large catalogs that generate thousands of facet combinations and search routes. This section provides a safe Liquid template, practical rules for blocking filters and internal search, and validation steps with Search Console to reduce crawl waste without losing important pages.
TLDR
Brief technical note
robots.txt.liquid is the template that generates the robots.txt file in Shopify; it serves to customize rules per store without touching CDN infrastructure. PIM is a centralized catalog management system; it matters because canonical URLs originate from it. sitemap.xml is the index of URLs that helps search engines prioritize crawling. rel canonical is the HTML tag that indicates the preferred version of a page and avoids duplication.
Shopify serves a default robots.txt but allows editing robots.txt.liquid for advanced adjustments. The golden rule: block only what adds no value to the main index and leave rendering resources accessible.
Context
Facets and filters produce infinite combinations that bloat the catalog and consume crawl budget.
How to approach it
Prioritize blocking routes identifiable by query patterns that should never rank, such as internal searches, filters with IDs, and collection pagination. Complement with rel canonical in collection templates to point to the main version and meta noindex where appropriate.
Example
Disallow user-agent star Disallow /search Disallow /*q= Disallow /*filter= Disallow /*sort= Disallow /*page=
Typical error
Blocking parameters without checking canonicals can prevent indexing of valid versions that use the same parameters.
Context
Google needs resources to render and evaluate each page; blocking them harms ranking.
How to approach it
Do not block theme CSS and JS files, product image routes, sitemap.xml, or main product and collection routes you want indexed. If your PIM exports a feed, ensure the feed URL and the routes it contains are accessible.
Example
Allow /assets Allow /images Allow /sitemap.xml Allow /products Allow /collections
Typical error
Blocking assets causes Search Console to show rendering issues and Google to incorrectly evaluate the page.
Context
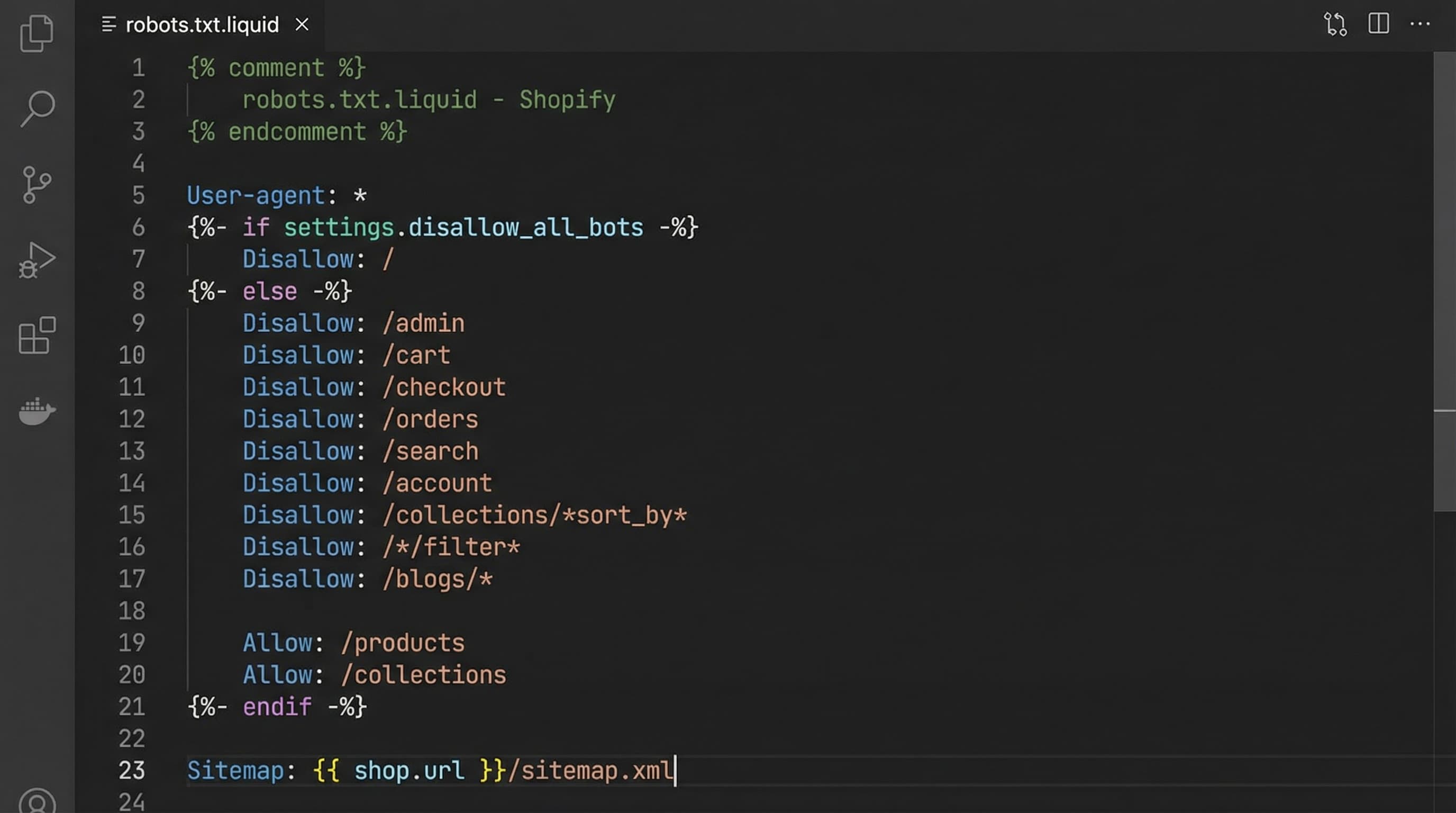
Below is a template ready to copy into robots.txt.liquid and adapt to your store's prefix.
How to approach it
Copy the template into a staging environment, adjust specific theme patterns, and document each Disallow with a comment. Keep rules conservative: better to add patterns gradually and validate impact.
Template example
User-agent: * Disallow: /search Disallow: /*q= Disallow: /*filter= Disallow: /*sort= Disallow: /*page= Allow: /products Allow: /collections Allow: /assets Allow: /sitemap.xml
Typical error
Pasting generic templates without replacing your theme's patterns can block valid routes and feeds.
Context
Verifying the robots file after editing prevents surprises in coverage and indexing.
How to approach it
Use the URL inspection tool and the robots file checker in Search Console to test specific URLs. Review the coverage report and crawl logs to detect URLs that Google visited and now ignores. If you correct rules, request public inspection of priority URLs to accelerate the new evaluation.
Example
Test a product URL in Search Console and verify it does not appear blocked by robots nor presents rendering errors.
Typical error
Not requesting a new inspection after the change and assuming Google applied the new version.
Quick checklist and best practices
Sources
Robots directives and best practices guide
How to access and edit theme files in Shopify
Robots.txt in Shopify is the first barrier to control what search engines crawl in a large catalog. In stores with many facets and filters, a poorly configured robots.txt increases crawl waste and can cause indexing of low-quality or duplicate pages. This step-by-step guide shows how to implement safe changes in the Shopify theme editor and validate them without risks.
Follow this minimum flow to apply changes without interrupting indexing: duplicate the theme, edit robots.txt.liquid in the copy, test specific routes with Search Console, and deploy to production only when tests pass.
Why it matters A quick rollback avoids downtime and indexing errors after changes to the rules file. How to approach it In the Shopify dashboard open Online Store themes, duplicate the active theme, and work on the copy. Keep a clear name with the date and note changes in the team changelog. Brief example Duplicate theme and rename backup-robots-2026-01-15 Typical error Editing the active theme directly without a backup
Why it matters The robots.txt.liquid file allows customizing rules per theme and blocking filter patterns without editing every URL. How to approach it Open the theme code editor and locate robots.txt.liquid. Add Disallow rules for typical facet and pagination parameters and keep Allow for static files and sitemap.xml. Use simple patterns and avoid general blocks that include product or collection routes. Brief example User-agent: * Disallow: /search Disallow: /?q= Disallow: /?sort= Allow: /sitemap.xml Typical error Blocking /collections or /products, which prevents indexing of valid pages
Technical note Shopify metafields are custom fields that store additional product data; they matter because they alter what is shown on the page and can generate content variations. PIM is the system that centralizes catalog attributes; it matters for maintaining consistency. Feed is the file you export to marketplaces; it controls which URLs are shared.
Why it matters Validation avoids launching rules that accidentally block crawling of important content. How to approach it Use the robots testing tool in Google Search Console and URL inspection to check specific routes. Google's official documentation on robots helps to understand syntax and Shopify's guide provides practical notes Brief example Test /search?q=sneakers and /products/my-sku to confirm behavior Typical error Trusting external simulators without checking the real response from Search Console
Robots.txt in Shopify requires validation and monitoring to avoid accidental blocks that reduce visibility and sales. Robots.txt is a file that tells crawlers which routes they should not visit and helps control crawl budget. Search Console is Google's tool to check indexing and technical errors and allows simulating rules. Sitemap is the list of URLs you prioritize for indexing. Crawl budget is the amount of resources Google allocates to crawl your site, critical in large catalogs.
Consult Google's guide for the robots.txt tester and Shopify's documentation on robots.txt
Context why this step matters The tester allows you to know if a URL is blocked by the rules and with which user agent it occurs. How to approach it Paste the provisional version of robots.txt into the tester and test representative routes: home, a collection, a product, feeds, and URLs with filter parameters. Complement with URL Inspection to verify rendering and exclusion reason. Brief example Test a collection URL and a URL with multiple filters to confirm they are not blocked. Typical error Checking only the home page and omitting catalog routes with parameters
Context why this step matters A well-planned block reduces crawl waste; an erroneous block can leave commercial pages unindexed. How to approach it Compare Crawl Stats and the Coverage report before and after the change. Filter by Excluded pages and the reason Blocked by robots txt. Keep a change log with dates and rules applied to facilitate correlation with variations in crawling and impressions. Brief example Detecting a drop in crawling on category pages after adding a Disallow rule that affected a shared folder. Typical error Taking a drop in crawling as a penalty signal without reviewing robots.txt or server logs
Context why this step matters Quick detection avoids loss of visibility and potential revenue drops. How to approach it Watch for increases in pages excluded by robots txt, coverage errors, and drops in impressions in Search Console. Recovery steps: revert the suspicious rule, use URL Inspection to request indexing, resubmit sitemap, and review crawl logs. Coordinate with product to deploy urgent fix if many URLs are affected. Brief example Revert a Disallow line that blocked collections and request re-indexing. Typical error Not correlating changes in robots.txt with alerts in Search Console and acting late
Optimizing the robots.txt file to control crawling is just one piece of the puzzle. It is useless to send bots to the right pages if the content of those pages (titles, descriptions, metafields) is not optimized to convert and rank. In extensive catalogs, manual management of product data quality is unfeasible. ButterflAI solves this challenge by allowing eCommerce teams to generate and optimize product content at scale with AI, ensuring that every URL you allow to be crawled is ready to compete in search results.
Go deeper with guides and tools connected to this topic.
Quick answers to common questions.

Discover a governance-first workflow to create high-intent product FAQs from real customer data, deploy safely, and measure SERP CTR impact.
Feb 20, 2026
Technical guide to choosing the best SEO app for Shopify, evaluating impact on Core Web Vitals, indexation, and catalog scalability without technical errors.
Feb 7, 2026
Learn how to manage discontinued products to avoid Soft 404 errors and maintain your authority with strategic 301 redirects.
Feb 2, 2026