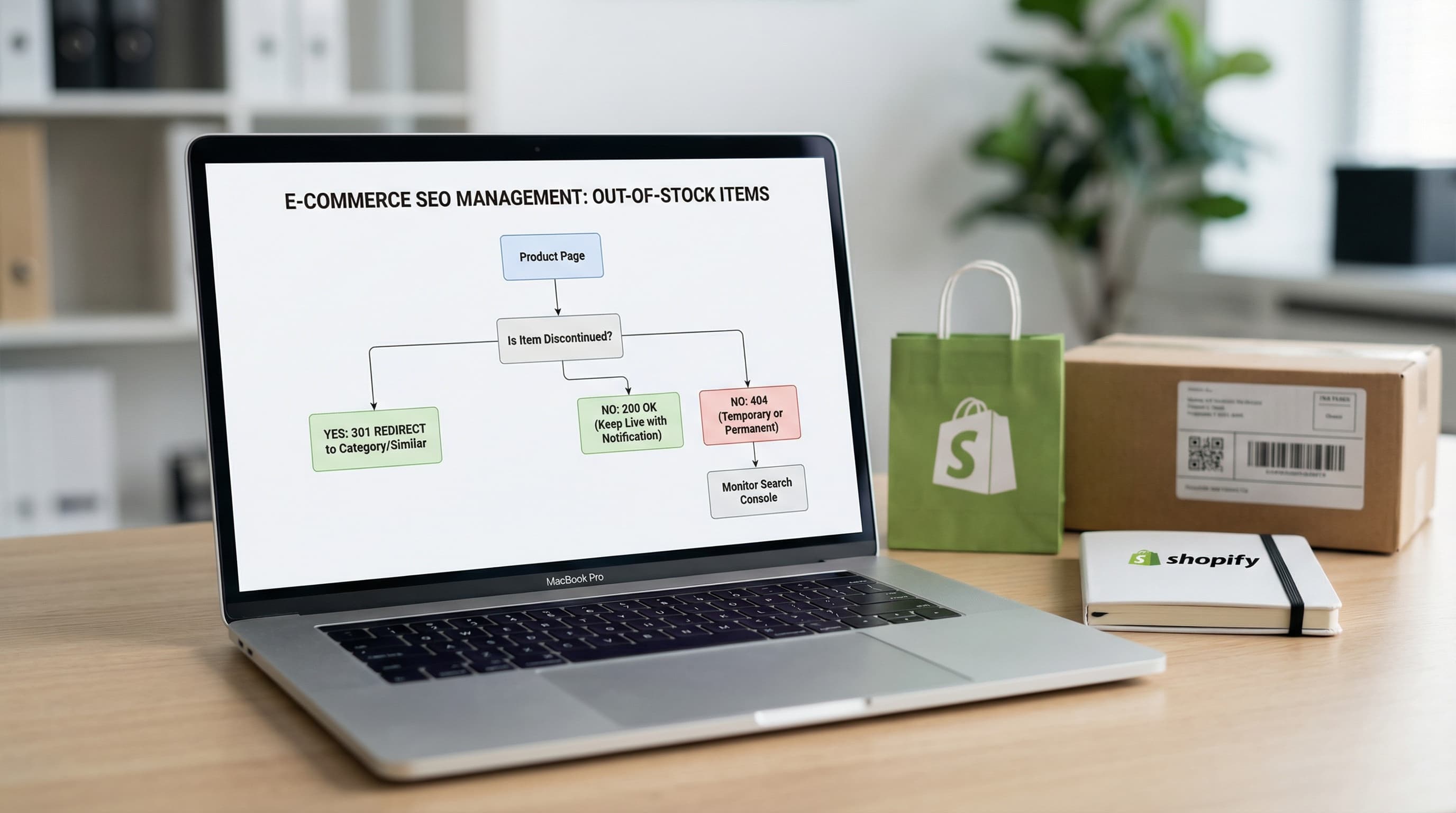
SEO Management for Out-of-Stock Products on Shopify: Guide & 301 Redirects
Learn how to manage discontinued products to avoid Soft 404 errors and maintain your authority with strategic 301 redirects.
Feb 2, 2026
Technical guide to choosing the best SEO app for Shopify, evaluating impact on Core Web Vitals, indexation, and catalog scalability without technical errors.
A Shopify SEO app can automate repetitive metadata, redirect, and sitemap tasks, but it has clear limits when improvement requires changing the HTML served by the theme or how critical resources are loaded.
If the intervention affects rendered HTML or priority resource delivery, the solution usually lies in modifying Liquid; if the goal is massive catalog processing, feed management, or Search Console integrations, an app provides the necessary scalability.
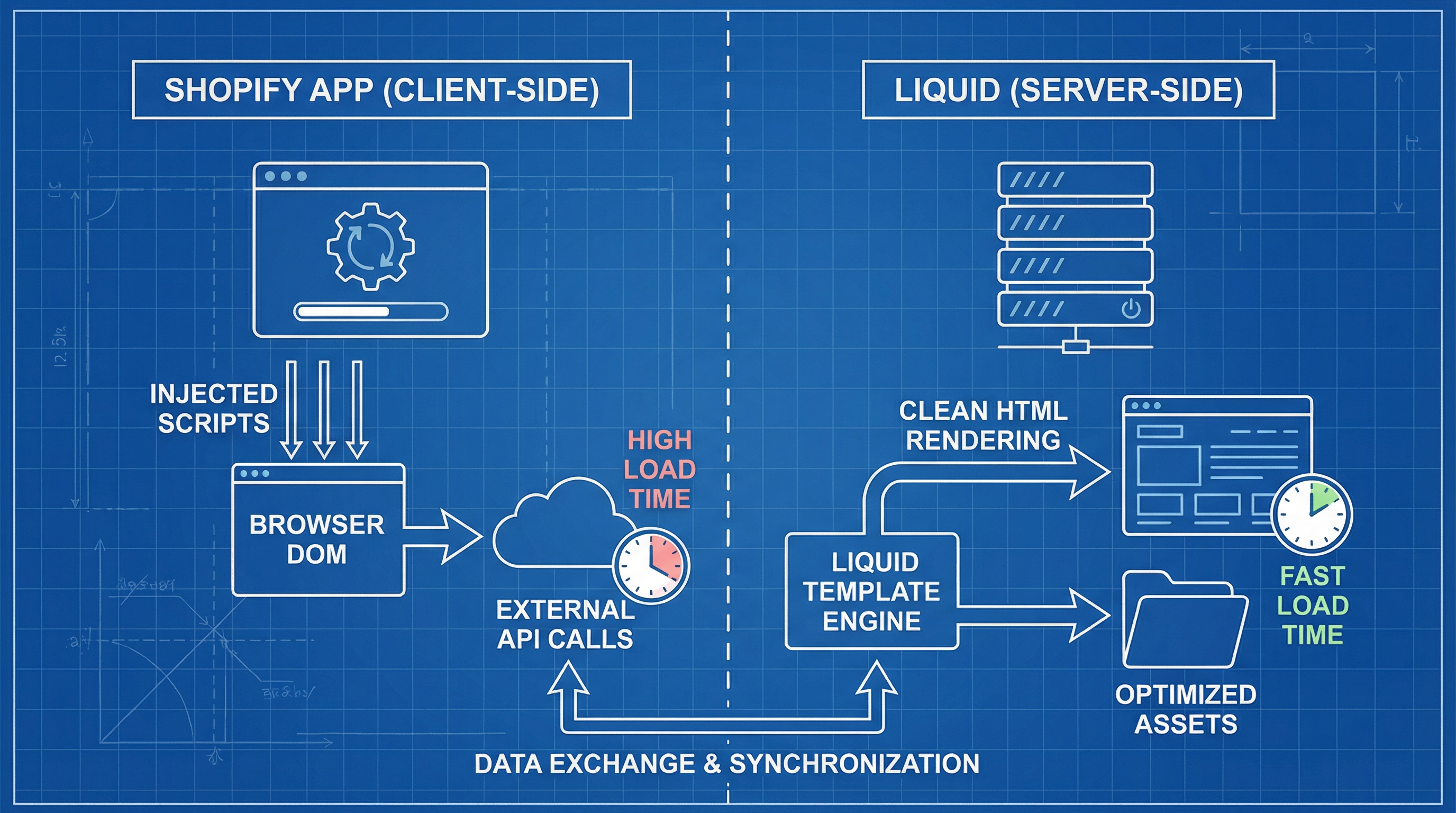
Apps facilitate operations at scale that would otherwise be manual or impractical.
How to approach it: An app is ideal for batch generating metatags, creating and maintaining sitemaps, managing bulk redirects, and synchronizing structured schema. Schemas are tags that describe content for search engines, improving interpretability. Likewise, apps can add extra fields to the catalog when a PIM (Product Information Management) system—which centralizes attributes and improves catalog quality—is unavailable. They are also useful for integrating with Search Console and feed generators (structured files exporting data to marketplaces).
Example: A rule that automatically applies title and description templates to 10,000 SKUs.
Typical error: Believing an app alone will solve HTML delivery performance issues when its main function is data management.
Structural problems exist that are only corrected by changing theme templates.
How to approach it: If LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) is slow due to unoptimized images, poorly implemented lazy loading, or scripts injected into the header, the solution involves editing Liquid and optimizing assets. Liquid is Shopify's template language controlling the HTML sent to the client; working directly on it allows ordering loading and serving responsive images from the server. For more on this, check the official Core Web Vitals guide.
Example: A theme loading third-party scripts before main content, elevating LCP, cannot be fixed by an app acting only on the client side.
Typical error: Installing an app to improve speed metrics without previously auditing the theme.
The decision depends on whether the improvement affects the initial DOM or data management at scale.
How to approach it: Implement in Liquid when you need to control <picture> tags with sizes and srcset, remove duplicate markup, or adjust H1/H2 semantics in templates. Use an app when the work implies massive catalog transformations, sitemap generation, or synchronization with PIM and feeds.
Example: Rewriting the product-template snippet to serve responsive images from HTML instead of injecting them later with JavaScript.
Typical error: Using an app that injects tags at runtime instead of serving optimized HTML from Liquid.
Many app claims mix on-page SEO concepts with unrealistic marketing promises.
How to approach it: Verify if the app injects scripts into <head> or <body>, if it requires blocking script tags, and always request a changelog. If they promise to remove duplicate content, ask if they act via canonicals or redirects and what rules apply. It is vital to use tools like Lighthouse to measure real impact before and after installation.
Example: An app promising to improve load speed but adding a script that blocks First Contentful Paint.
Typical error: Making installation decisions based solely on marketing screenshots without testing in a staging environment.
This is an actionable list to decide with technical criteria before compromising the production environment.
How to approach it: Execute these steps in staging and document results.
<head>.Example: Measure LCP and CLS on a standard product page before and after activating the app.
Typical error: Uninstalling an app without removing code remnants that leave traces and continue affecting performance.
Practical Conclusion: Prioritize Liquid changes when improvement impacts performance or essential markup. Employ apps for mass automation, feeds, and integrations. Always audit in staging, request technical evidence, and document changes to avoid breaking indexation or Core Web Vitals.

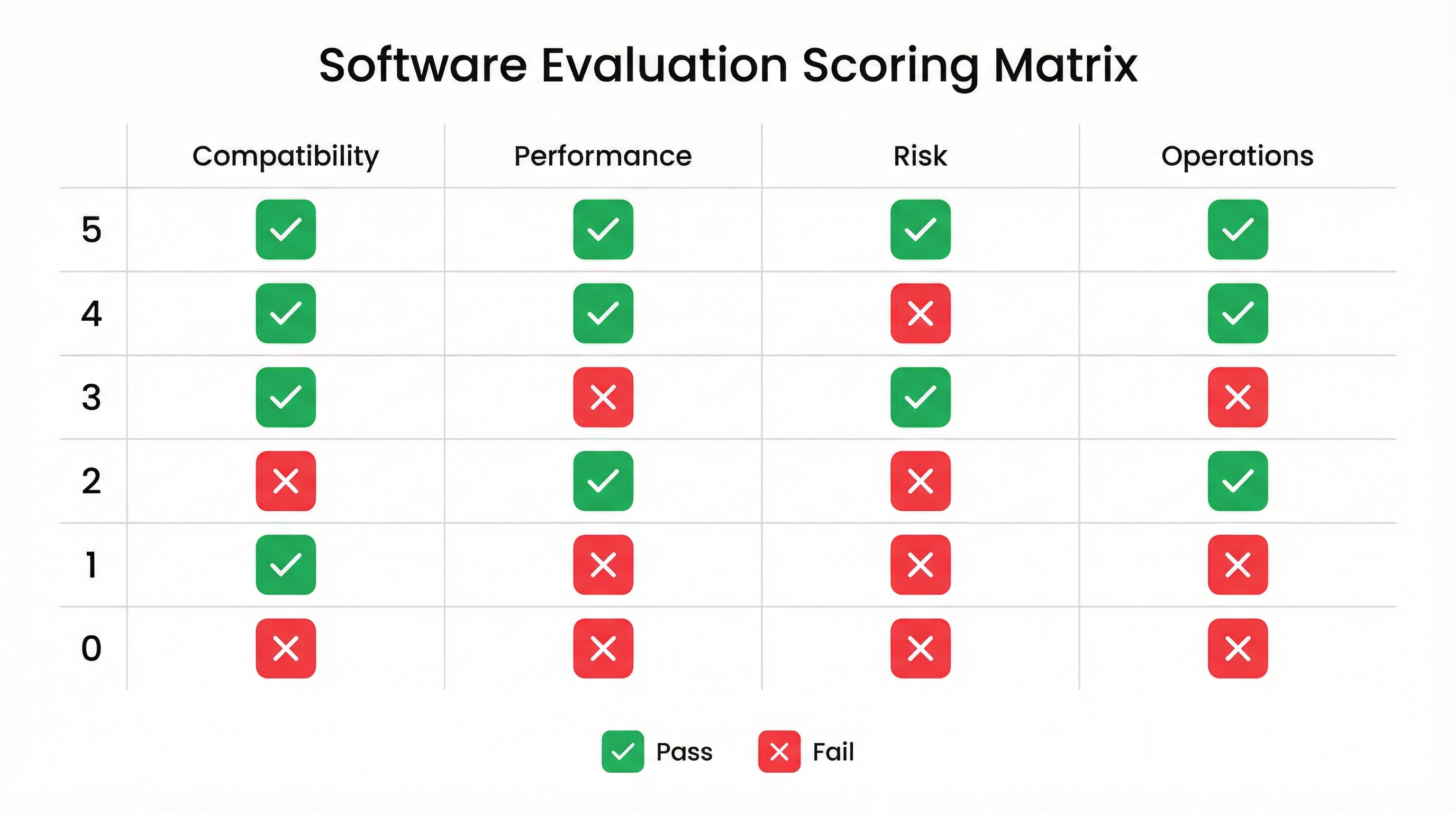
In 30 minutes, you can evaluate if a Shopify SEO app adds value or introduces technical risk harming indexation and Core Web Vitals. This framework proposes quick scoring with concrete evidence to decide whether to install, test in staging, or discard.
TL;DR: Apply five key criteria and score 0 to 5 for each (total sum 0 to 25). A practical recommendation is to demand a minimum of 18 for staging tests and 22 to move to production. If the app modifies canonicals, redirects, or injects scripts, assign penalties and demand tests with Search Console and PageSpeed Insights.
Why it matters: Avoiding incompatibilities drastically reduces the risk of breakage after installation.
How to approach it: Review permissions in Shopify admin and ask for a trial in a staging environment. Verify if the app edits templates, adds global scripts, and is compatible with Online Store 2.0. Shopify metafields are custom fields for products and collections allowing SEO data storage without touching templates, facilitating rollbacks. Consult Shopify's official documentation to check expected template behavior.
Example: An app overwriting the theme to inject scripts increases risk; ask it to use page-loaded snippets.
Typical error: Installing in production without theme backup or prior testing.
Why it matters: Incorrect changes to canonical and meta robots can deindex critical pages from results.
How to approach it: Request documentation on canonicalization rules, pagination, and query string handling. Test in staging and use Search Console's URL inspection tool to verify results.
Example: If the app applies a collection's canonical to products, the category may lose visibility due to erroneous consolidation.
Typical error: Trusting default settings without checking variants and pagination.
Why it matters: External scripts and blocking rendering degrade LCP and CLS, affecting mobile experience.
How to approach it: Install in staging and run Lighthouse and PageSpeed Insights to measure before and after. Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, and INP) summarize load experience and visual stability. Prioritize apps offering asynchronous loading (defer) or server-side rendering for structured data markup.
Example: An app injecting JSON-LD via JavaScript can increase CLS and delay LCP on mobile.
Typical error: Not measuring Core Web Vitals on real mobile devices and relying only on desktop.
Why it matters: An app must allow massive and efficient changes for large catalogs.
How to approach it: Evaluate compatibility with your PIM and if it supports bulk import via CSV or APIs. Remember a PIM centralizes attributes to maintain catalog quality and scale.
Example: An app forcing product-by-product title and meta description editing is not viable for catalogs with thousands of SKUs.
Typical error: Choosing an app for a pretty interface (UI) instead of its API support.
Why it matters: Objective scoring accelerates decision-making and reduces operational risks.
How to approach it: Assign 0 to 5 points per criterion and document evidence in an evaluation sheet. Low scores require rollback tests and strict monitoring.
Example: A score of 20 with high performance risk implies installing only in staging and blocking deployment until script loading is optimized.
Typical error: Deploying without a rollback plan or continuous monitoring.
If you have just installed a Shopify SEO app and need to confirm it hasn't broken indexation or worsened Core Web Vitals, this post-installation audit offers actionable steps, Search Console checks, and a clean uninstallation plan. This applies especially to scalable catalogs and stores using PIM or metafields.
TL;DR:
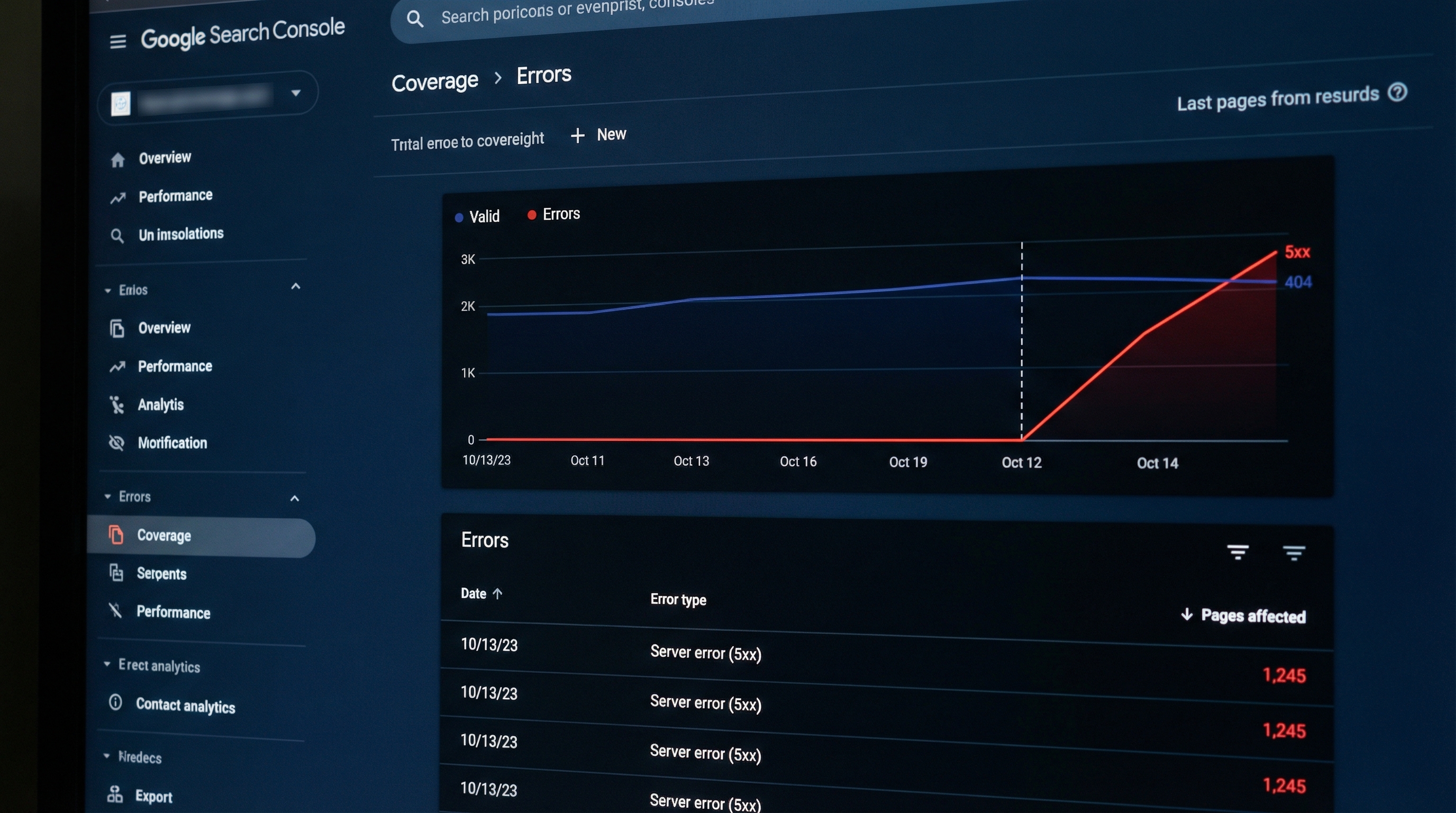
Why it matters: An app can inject scripts, change metadata, or modify liquid templates in ways that affect indexation and user experience. Detecting it quickly mitigates traffic loss.
How to approach it:
noindex.Example: Filter by date (e.g., installation on 01/17/2026) to see a possible increase in pages excluded by noindex in product templates.
Typical error: Attributing traffic variations to the app without validating seasonality or other active campaigns.
Why it matters: App widgets and scripts are the most frequent cause of worsening LCP and CLS.
How to approach it:
Example: Lighthouse shows increased LCP due to a review script blocking rendering. Solution: load the asynchronous version or render server-side.
Typical error: Trusting only lab tests without comparing with real user experience.
Why it matters: Changes in canonicals, sitemap, and meta robots affect mass indexation and can generate duplicates.
How to approach it:
noindex.Example: You detect a canonical pointing to the version with a query string. Correct the template and regenerate the sitemap.
Typical error: Forgetting to regenerate or resubmit the sitemap after making massive changes.
Why it matters: Uninstalling an app without cleaning up leaves orphan assets and snippets that keep loading, affecting performance and indexation.
How to approach it:
Example: When removing a reviews widget, delete the reviews.liquid snippet, the reviews.js asset, and check that no {% include %} remains in the product-template.
Typical error: Deleting the app from admin but not deleting the code asset, generating 404 errors and penalizing performance.
Choosing the right tool is just the first step; maintaining data quality is the ongoing challenge. ButterflAI detects improvement opportunities in your catalog and generates SEO-optimized content (titles, descriptions, and metadata) at scale, ensuring your listings' technical structure boosts indexation without adding unnecessary load to your store.
Quick answers to common questions.

Learn how to manage discontinued products to avoid Soft 404 errors and maintain your authority with strategic 301 redirects.
Feb 2, 2026
Optimize your store navigation and improve rich results with this technical breadcrumb guide for Shopify.
Jan 24, 2026

Technical guide to optimize LCP, CLS, and INP on Shopify, reduce load times, and maximize conversion with an efficient asset strategy.
Jan 23, 2026