Amazon A+ Content: How to Scale It with Catalog Data
Operational playbook to convert Shopify/PIM attributes and metafields into reusable and scalable A+ modules.
Feb 4, 2026
Technical and operational guide to master structured data markup, improve CTR, and scale your UGC without penalizing load speed.
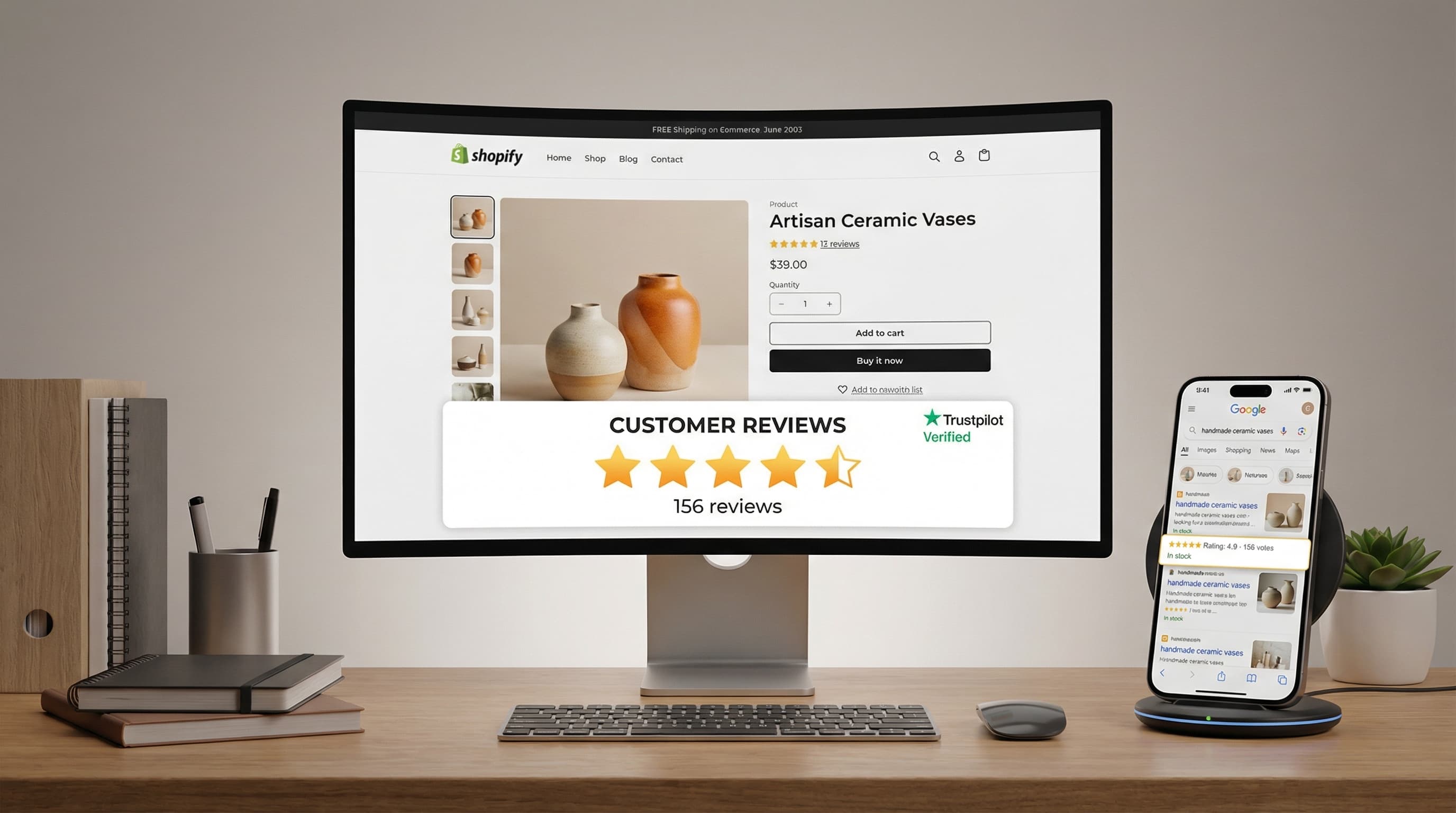
Shopify reviews are a direct lever for trust and organic CTR: when Google displays star ratings in search results, click-through rates often improve, and users perceive less risk when buying. For eCommerce and SEO teams, this turns UGC (User Generated Content) into a strategic source of traffic and conversion that deserves clear quality and markup rules.
Choosing how to implement reviews is a technical and operational decision: using an app from the ecosystem, a native solution based on metafields, or a headless approach connected to a PIM. Each alternative has advantages and costs regarding markup control, performance, and scalability.
To understand the necessary infrastructure:
Include an audit in Search Console to detect errors in Review and AggregateRating, and consult the official Google guide on review snippets for requirements and examples.
To scale, define moderation rules, duplicate control, and a bulk import process with mapping to metafields; avoid injecting markup into pages that do not represent a real product. A typical error is adding ratings to generic pages or collection listings that do not meet Google's requirements, which can invalidate your rich results.
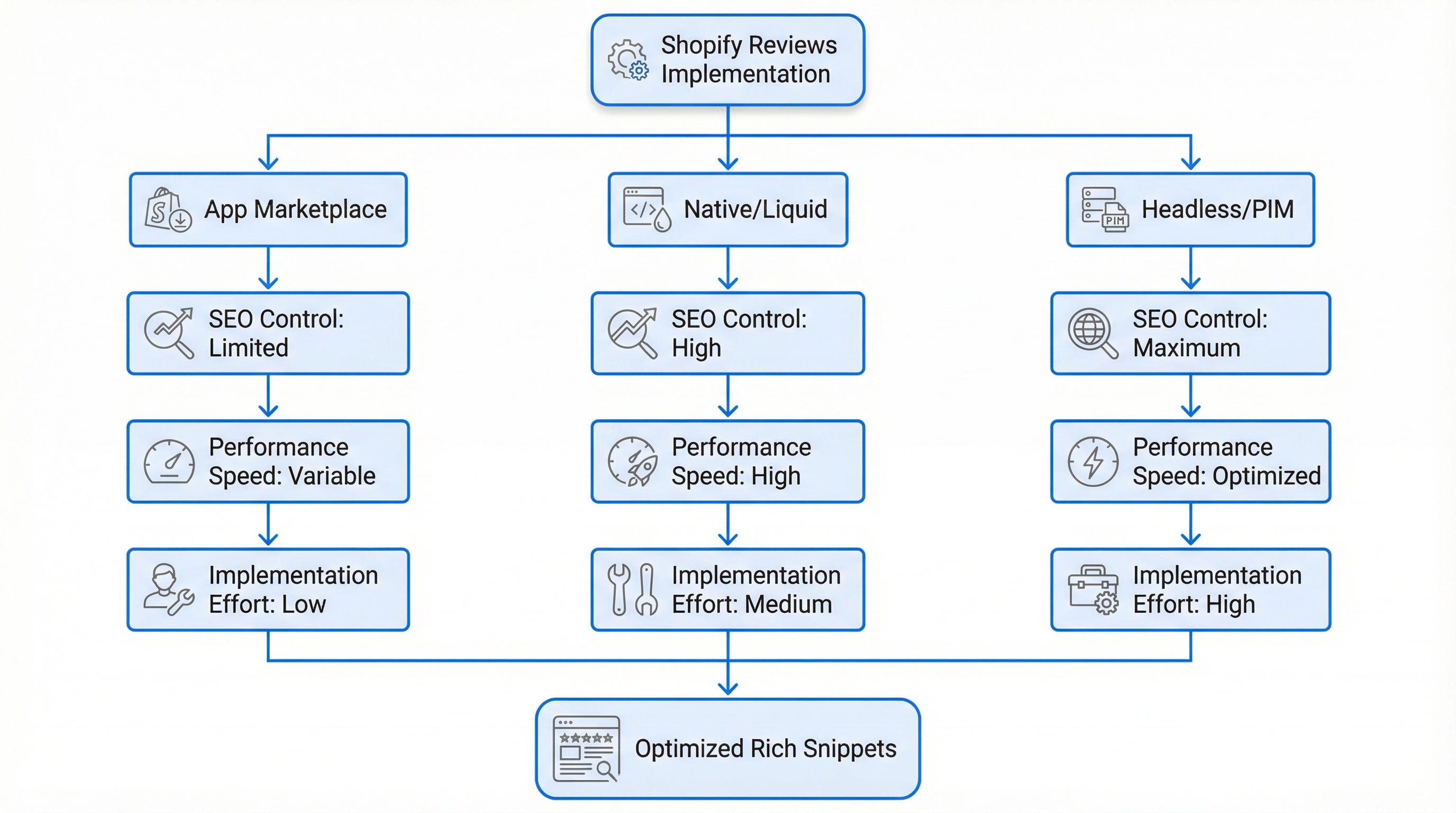
Shopify reviews are a direct lever to gain trust and improve organic CTR when Review and AggregateRating markup is well-implemented and the solution does not degrade speed. This practical guide helps decide between a marketplace app, native integration, or headless architecture based on three criteria: markup SEO, impact on Web Vitals, and legal compliance.
Choosing the right architecture avoids redoing integrations and facing SEO and performance issues in later stages.
How to approach it:
Example: A SaaS app sends webhooks to your PIM, and your server injects JSON-LD server-side into the product template. Avoid choosing an app that only injects markup into the client DOM via heavy JavaScript.
Google displays stars only when Review or AggregateRating are valid and crawlable.
Prioritize apps that generate JSON-LD server-side or allow inserting JSON-LD into the product template to include properties like ratingValue and reviewCount. Avoid relying exclusively on client-side rendering, as Googlebot sometimes does not execute full JS before indexing. Review the technical vocabulary at Schema.org AggregateRating.
Example: Adding JSON-LD server-side with itemReviewed, ratingValue, reviewCount, and bestRating inside the product HTML, instead of showing only the visual widget without accessible structured data.
Poorly implemented external widgets and scripts can increase LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) and affect visibility and conversion.
Choose solutions that offer lazy loading and asynchronous loading, and that allow disabling CSS and scripts on templates that do not show reviews. In headless environments, serve minimal HTML and request reviews via API to render on the server. Measure the impact with Core Web Vitals.
Example: Disable the heavy embedded widget and consume the reviews API to produce static HTML with stars on the server, avoiding unnecessary scripts during initial load.
The Omnibus Directive requires transparency regarding paid reviews and traceability. Choose solutions that export origin metadata and allow moderation rules via API. Implement purchase verification and tag imported reviews with source. You can consult the legal text of the directive.
Example: Adding a source field with values like marketplace, import, verified_purchase, and showing a visible badge ("Verified Purchase") when transactional evidence exists. Avoid mixing imported reviews and pure UGC without recording their origin.
Quick Selection Checklist:
Distinguishing the markup type avoids sending contradictory signals to Google and reduces errors in Search Console. Below, we detail how to implement markup without breaking the schema and how to audit common failures.
Use Review for individual reviews with author and date, and AggregateRating for the aggregate product score.
author, datePublished, reviewBody).ratingValue, reviewCount, bestRating).Consult the specifications at Schema.org Review.
Example: Implement aggregateRating with ratingValue: "4.3" and reviewCount: "215", and publish three individual Review items with author and datePublished visible on the listing. A typical error is marking an aggregateRating without reviews being visible or without a numerical count on the page.
The injection format affects maintenance and load speed. I recommend JSON-LD injected from the theme or via metafields that consolidate data into a single script. JSON-LD is a format inserted as a script, avoiding mixing markup with visible HTML, which reduces the chance of breaking the design when adjusting SEO.
In Shopify, adding it in the product.liquid template or via metafields avoids duplicates. If using apps, validate that they do not generate redundant scripts (microdata + JSON-LD) causing conflicts.
Example: A clean JSON-LD script including itemReviewed of type Product and aggregateRating with reviewCount synced with visible reviews.
Google only generates rich snippets if the data is complete and consistent. Ensure ratingValue, reviewCount, and itemReviewed are correct. Reviews must be real and displayed on the page. Validate with the Rich Results Test tool and URL inspection in Search Console.
Example: Checking that reviewCount is greater than zero, that ratingValue is numerical, and that listed reviews match the JSON-LD. Avoid numerical values encoded as text.

Maintaining authorship, date, and provenance preserves credibility and avoids schema discrepancies. When exporting reviews from another platform, include author, datePublished, reviewBody, and a unique ID. Import via CSV to metafields or the PIM. Maintain an origin field for internal auditing.
Example: CSV with columns author, datePublished, rating, reviewBody, origin (original platform) and map to product.metafield.reviews. Do not overwrite the original date with the import date.
Controlling spam and fake reviews protects schema quality and brand perception. Define blocking rules for duplicate links, minimum length, and email verification. Automate pre-filtering and keep a manual approval flow for exceptions.
Example: Automatic rule to block reviews with external links (potential spam) and those under 25 characters pending manual review. Publishing reviews without filters increases low-quality content signals.
Quick Implementation Checklist:
aggregateRating and Review match what is visible.Reviews in Shopify need to preserve metadata and formatting for markup to work and to avoid losing the trust of historical customers. This section explains how to prepare the CSV, map fields, and enrich metadata.
Exporting from the source preserves integrity and traceability. Request or generate a CSV with columns author, content, rating, date, product_id, source_id, and media where applicable. Ensure UTF-8 encoding and dates in ISO 8601 format. If you manage a PIM, remember it is the ideal central system for managing this synchronization.
Example: author: "Nicolas", content: "Good", rating: "5", date: "2025-01-15", product_id: "SKU123", source_id: "ext123". Avoid dates in local formats (DD/MM/YY) that break the import.
Platforms use different names for the same properties. Create a master map that transforms source columns to destination and adds source_id to avoid duplicates. Use scripts (Python or Power Query) to clean residual HTML, normalize scores, and remove special characters.
Example: Map user_name to author and stars to rating. Duplicating reviews due to the absence of a unique external identifier is a frequent error.
Search engines require well-formed data. Add date in ISO 8601 with time zone, author.name, reviewBody, and a product identifier matching the SKU in Shopify.
Example: date: "2025-01-15T12:00:00Z". Omitting author.name or using dates without a time zone will prevent correct validation.
Importing without control can degrade trust and SEO. Import via the review app or API and apply automatic rules for spam and minimum length.
Quick Import Checklist:
source_id.author.name, reviewBody, and media.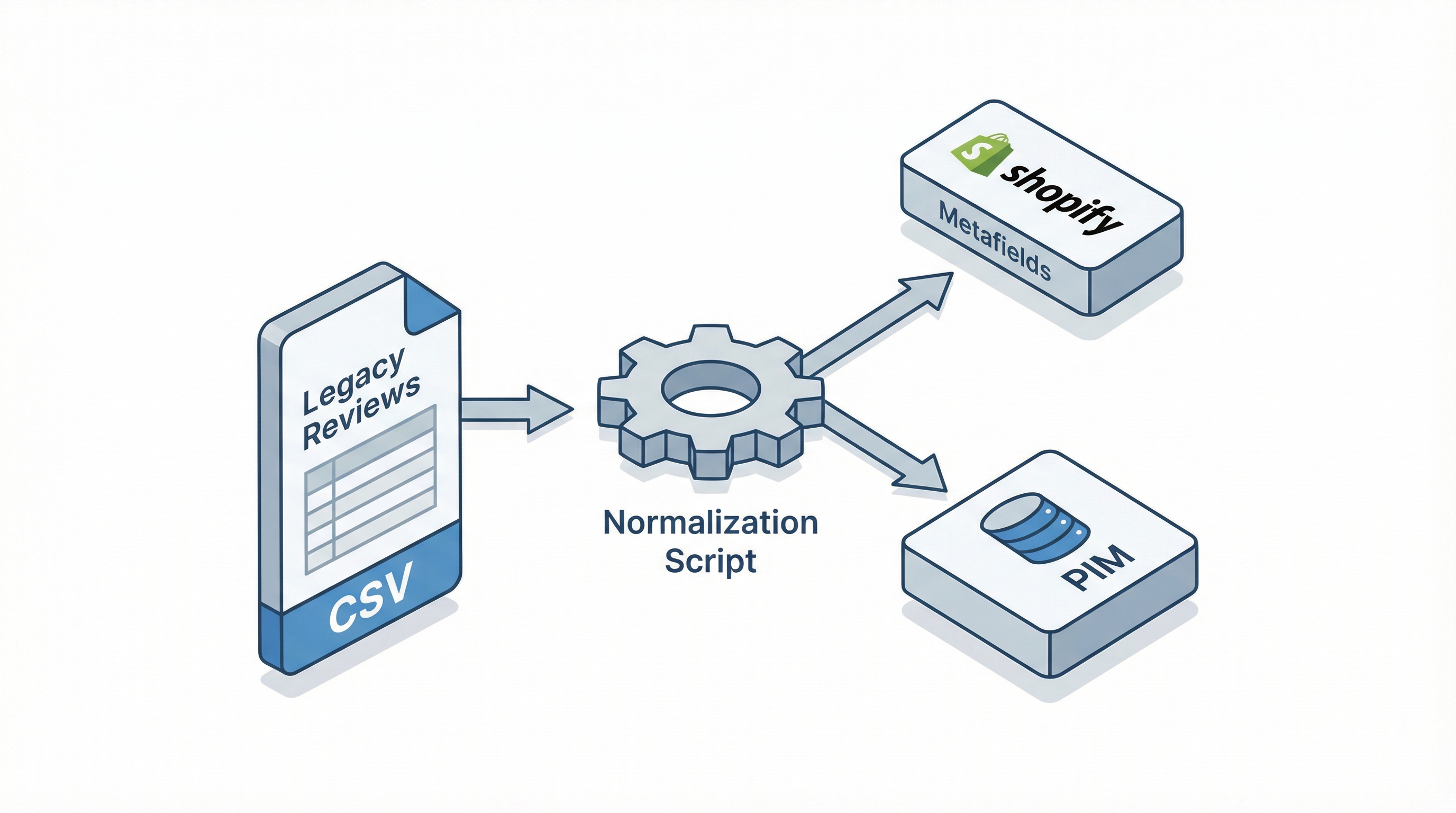
When scaling UGC, you need clear rules to avoid noise, abuse, and markup issues that can break your schema.
Moderation prevents spam, offensive language, or fraudulent reviews from damaging catalog reputation. Combine automatic filtering with human reviews on critical signals.
Implement simple rules in a review queue: extreme scores, reviews with links, blocked words, and new users with suspicious history. Use automatic filters to block or flag content and keep a small human operation for ambiguous cases.
Example: Reject reviews containing URLs or more than three words from the "block list"; escalate to the team if the author has fewer than two verified purchases. Relying only on manual moderation when volume grows creates latency and ruins the experience.
Automatic sentiment analysis allows prioritizing inventory and detecting operational issues. Long review texts can be summarized and tagged with language models to extract sentiments (positive, neutral, negative) and themes like "shipping", "packaging", or "sizing".
Configure pipelines that process new reviews and update aggregated metrics feeding product dashboards.
Example: Send automatic alerts if the percentage of negative reviews about "sizing" exceeds 10% in seven days. Using AI as a sole moderator without safety rules can generate false positives.
Define public publication policies, review times, and an SLA for appeals. Maintain a change log and retention policy. For technical integrations, use verified feeds and do not modify schema markup directly on high-traffic pages without prior A/B testing.
Quick Governance Checklist:
To validate that reviews in Shopify generate impact, it is necessary to establish a baseline and measure changes within controlled time windows.
Organic CTR indicates whether the star snippet attracts clicks from Google. Compare CTR by product URL in Search Console before and after in 30 to 90-day windows. Example: A page goes from 2000 impressions and 40 clicks to 2500 impressions and 100 clicks; CTR rises from 2% to 4%. Be careful attributing the improvement solely to reviews if you have also changed titles or meta descriptions.
Reviews increase trust and reduce friction. Use analytics data to compare conversion per SKU, grouping by number of reviews and average rating. Example: Compare conversion of products with 0 reviews versus products with 10 or more reviews in the same period, controlling for channel and price.
The AggregateRating markup can show stars in results. Validate the markup with Rich Results Test and review coverage in Search Console. Consult the structured data guidelines.
Example: Audit 100 URLs and record how many are eligible for rich results. A typical error is marking reviews loaded only by JavaScript without Google indexing them correctly.
Negative reviews often stem not from a bad product, but from a bad description: incomplete data, poorly explained sizing, or incorrect expectations generated by listing content. If the base content of your Shopify catalog is not accurate, the best review system will only serve to amplify complaints about incorrect information.
ButterflAI detects inconsistencies in your product attributes and automatically generates optimized and enriched descriptions. By ensuring technical, visual, and SEO information is perfect before the sale, you reduce post-purchase friction and encourage positive reviews based on a product experience that delivers what was promised.
Quick answers to common questions.

Operational playbook to convert Shopify/PIM attributes and metafields into reusable and scalable A+ modules.
Feb 4, 2026

Operational guide to mastering synonyms, filters, and merchandising on Shopify to maximize conversion.
Jan 29, 2026

Master your Shopify category SEO with a content strategy, technical architecture, and smart scaling.
Jan 17, 2026