How to Choose and Audit a Shopify SEO App Without Breaking Your Technical SEO
Technical guide to choosing the best SEO app for Shopify, evaluating impact on Core Web Vitals, indexation, and catalog scalability without technical errors.
Feb 7, 2026
Guide for eCommerce Managers: why remove meta keywords and how to prioritize tags that actually improve your CTR and rankings.
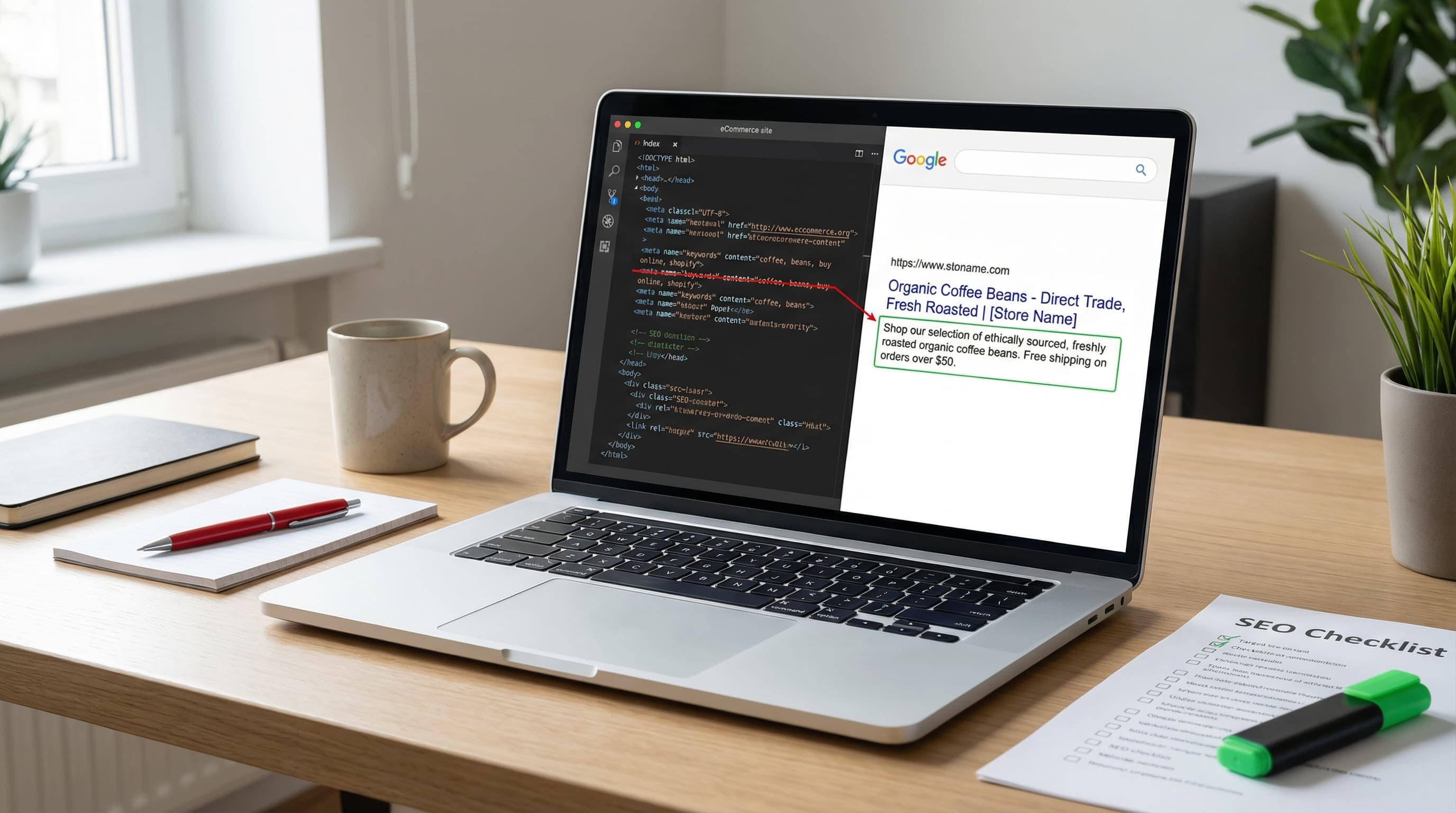
TL;DR: Meta keywords stopped having value for ranking years ago, yet they continue to generate noise and manual work in online stores. Detecting and removing them saves time and reduces spam and duplication risks.
The meta keywords tag is a remnant of classic SEO that, in practice, does not influence rankings in major search engines. In 2009, Google confirmed it does not use it to rank results. Even so, many themes, migrations, and apps continue to generate them for compatibility or due to outdated templates.
Modern engines rely on content signals, links, and structured data to understand intent. Maintaining meta keywords adds no value and can introduce noise into data pipelines and marketplace exports.
To understand the scope of the problem, aligning technical terminology is necessary:
Instead of investing time in meta keywords, reallocate effort to optimizing title tags and meta descriptions to improve CTR, implementing structured data on PDPs for rich snippets, and improving content quality in listings and collections. Audit templates and apps for meta keywords, document the sources injecting them, and remove automatic injection.
The meta keywords tag no longer provides SEO value in most search engines and can even reveal product strategy when used indiscriminately. In this practical comparison, we will see what each element served for, why to stop investing time in meta keywords, and where to reallocate that effort to improve on-page CTR and positioning.
Context: Why this step matters Meta keywords were an early attempt to indicate a page's keywords to search engines.
How to approach it Today, most search engines ignore meta keywords due to abuse and spam. Keeping them can expose internal product lists and categorizations that competitors can read from the HTML. Instead of optimizing meta keywords, remove the tag from the theme or apps injecting it and document in your audit which modules generated them.
Brief example
Entry that must be removed from head: name='keywords' content='sneakers, running sneakers, trail sneakers'
Typical error Leaving meta keywords filled with long lists copied from the PIM.
Context: Why this step matters The title tag is the primary tag influencing ranking and the first impression in search results.
How to approach it Optimize titles focused on commercial intent and variations by page type. For PDPs, use brand, product name, and main variant. For collections, use search intent and differentiating attribute. Keep length readable for the user and avoid stuffing with repeated keywords.
Brief example
Title for PDP: Brand | Product Name Variant | 5.0 ⭐
Typical error Automatically generating titles with senseless concatenations from PIM fields.
Context: Why this step matters The meta description does not directly affect ranking in many engines but does impact CTR from the SERP.
How to approach it Write descriptions summarizing benefit, offer, and call to action within 120 to 160 visible characters. Use dynamic data where it makes sense, such as availability or promotion, but avoid them being mere duplicates of the main content.
Brief example Meta description example: "24h shipping and free returns on this model. Buy now and save 10%."
Typical error Copying the first sentence of the product sheet without a commercial focus.
Removing meta keywords is just the starting point. There are alternatives with real impact on CTR and rankings:
Brief example Dev ticket: "Remove meta keywords from App X and add deployment validation to prevent reinjection."
Typical error Removing the tag without validating that it is not used for internal dependencies of some app.
To dive deeper, review this practical guide on meta keywords and their relevance in SEO.

Below is an operational checklist to locate hidden meta keywords in your Shopify store and decide on remediation. As a team, perform these five quick checks, remove the injections, and reallocate time to elements that actually improve CTR and visibility.
Meta keywords in eCommerce frequently appear in legacy stores. Although major search engines do not use this meta tag for ranking, its presence is often a symptom of obsolete code or apps injecting meta tags, potentially generating duplicates or contaminating feeds.
Why it matters: Confirms in minutes if there are visible meta keywords in the head.
How to approach it: Open a product page, select "view page source," and search for the string keywords. Repeat across various product templates, collections, and the home page. Check URLs with parameters and product variants to detect conditional injection.
Example: Locating a line <meta name='keywords' content='...'> where content is concatenated from product tags.
Typical error: Assuming a clean home page implies total absence when the tag may appear only in product templates.
Why it matters: Older themes build meta tags from global snippets.
How to approach it: In Shopify admin, open Online Store > Edit code and search in layout (files) and header snippets for words like "keywords" or "meta name". If working with version control, do a global search in the repository before touching files. Document modified files.
Example: A header.liquid snippet that iterates through product tags to fill a legacy meta keywords tag.
Typical error: Editing visible templates without reviewing globally included snippets that maintain the injection.
Why it matters: SEO, feed, or translation apps can add meta tags automatically.
How to approach it: Review the app list, open settings for those touching head or SEO, and disable meta tag functions. If you cannot disable, contact support. After any change, recheck the source code.
Example: A feed app adding meta keywords for compatibility with an old marketplace.
Typical error: Uninstalling the app without removing snippets it left in the theme, leaving residual code.
Why it matters: Language versions or dynamic templates may inject meta tags only on certain routes.
How to approach it: Test URLs in different locales and with product variants. If using a PIM, review its mappings and export templates (remember the PIM centralizes attributes and may export obsolete fields).
Example: Meta keywords appearing only in the foreign language version due to the translation app.
Typical error: Reviewing only the default version and overlooking locales containing the tag.
Why it matters: Removing the injection reduces noise and frees up time for effective optimizations.
How to approach it: Create a ticket with affected pages and source files, remove the injection from the snippet or app, deploy to staging, and test. After confirming cleanliness, prioritize generating dynamic titles and meta descriptions and adding schema for products.
Example: Replacing a meta keywords tag with a title template using brand and product type stored in metafields.
Typical error: Removing meta keywords without verifying if any feed or integration depended on that field.
Useful sources: Shopify theme editing documentation.
In eCommerce, it is common to find meta keywords in legacy themes or apps. Since they no longer contribute to positioning, this guide explains what to optimize instead, focusing on CTR and catalog relevance.
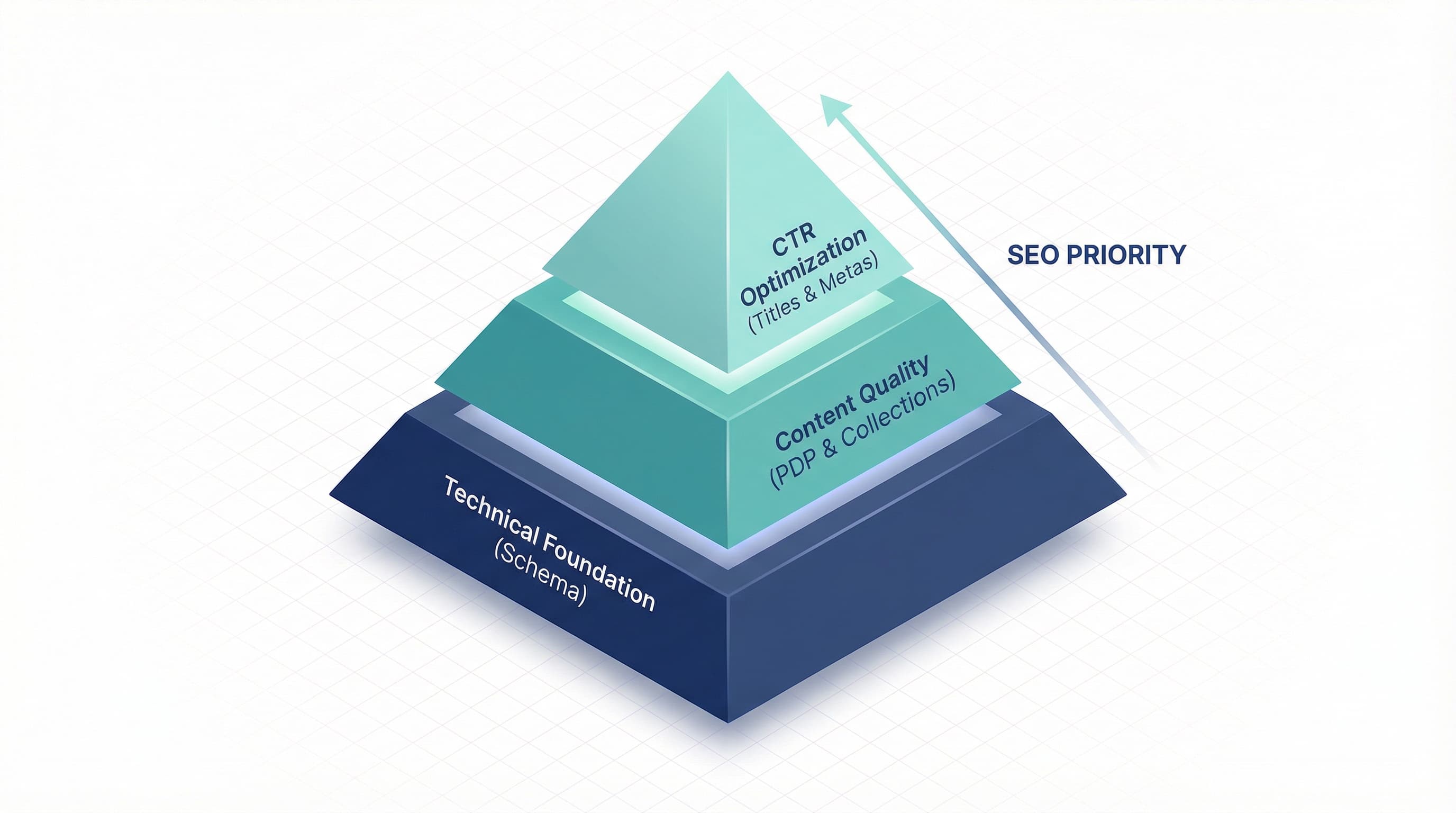
Prioritize in this order:
Why it matters: Title tags are the on-page signal with the highest impact on CTR and relevance from the SERP.
How to approach it: Apply templates by page type in the CMS or theme. In Shopify, use theme variables to compose titles per product like product.title and product.vendor. Keep titles between 50 and 60 visible characters in the SERP.
Example: Template: product.title - product.vendor | category
Typical error: Using long autogenerated titles with repeated keyword lists.
Why it matters: They influence CTR, which engines use as an indirect signal of relevance.
How to approach it: Write descriptions focused on benefits, call to action, and competitive advantage. Keep between 120 and 155 characters. In Shopify, you can use product.metafields or liquid filters to inject dynamic fragments.
Example: "Shipping in 24 hours and 2-year warranty. Buy now and save 15% with code."
Typical error: Repeating the title inside the description or leaving the field blank.
Why it matters: Schema allows search engines to show rich snippets (price, availability, ratings), increasing CTR.
How to approach it: Implement product schema in JSON-LD in product templates. If using PIM or feeds for marketplaces, ensure price, currency, and availability are synchronized.
Example: Including price, SKU, and rating in the PDP JSON-LD.
Typical error: Including inconsistent data between PDP and feed.
Why it matters: Useful content reduces bounce rate and helps understand purchase intent.
How to approach it: Prioritize unique descriptions, bullets with benefits, technical specifications, and usage examples. Use quality control from PIM or metafields to maintain standardization.
Example: List of bullets: materials, measurements, maintenance instructions.
Typical error: Descriptions copied from the manufacturer without commercial adaptation.
Why it matters: Optimized images improve accessibility and can rank in image search.
How to approach it: Name files with descriptive words, compress without losing quality, and add semantic alt text of 50 to 125 characters.
Example: Alt: men's running shoe non-slip sole blue size 42
Typical error: Empty alt or keyword lists.
Why it matters: They allow structuring additional product information (Metafields) and maintaining a single source of truth (PIM).
How to approach it: Define metafield templates for recurrent attributes and synchronize with PIM. Use those fields to enrich titles, descriptions, and schema.
Example: Metafield product.warranty with value "24 months" used dynamically in the meta description.
Typical error: Saving information in internal notes or titles and not in structured fields.
For large catalogs, the key is avoiding manual investment in meta keywords and reallocating effort towards intelligent automation of title tags, meta descriptions, and structured data.
The meta keywords tag provides no value and is noise in massive catalogs. Prioritize elements affecting CTR and SERP appearance.
Detecting if a theme or app is still injecting meta keywords is key to cleaning noise and avoiding conflicts. Scan theme templates and app outputs modifying the head. You can perform an automated sweep with scripts looking for meta name='keywords' and listing affected stores.
Brief example: Iterate through theme files searching for the string and generate a CSV report. Typical error: Forgetting to review SEO apps injecting tags via JavaScript snippets.
Controlled templates reduce manual work and maintain consistency. Define rules by category, brand, and feature to generate title and meta description with placeholders and length limits. Use priority rules not to overwrite manually validated fields.
Brief example: Template title Brand - Model - Key Attribute. If key attribute doesn't exist, use fallback short description.
Typical error: Templates that are too long and get cut off in SERP.
Automating with AI is effective if there are Quality Gates. Implement automatic checks for length, keyword cannibalization, and duplicates, and an approval flow for massive changes. Integrate with PIM or Shopify via API to apply meta tags and schema scalably.
Brief example: Daily report with items having low expected CTR and improvement suggestions for review by the Catalog Manager. Typical error: Blindly trusting massive replacements without A/B samples.
Eliminating meta keywords is just the first step to sanitizing your online store; the real challenge is scaling the creation of useful content (titles, descriptions, and attributes) that actually impacts conversion. ButterflAI detects optimization opportunities in your catalog, generates enriched content, and ensures your metafields and structured data are always ready to rank, without repetitive manual work. Instead of cleaning obsolete tags one by one, allow the system to audit and improve the quality of your listings continuously.
Go deeper with guides and tools connected to this topic.
Quick answers to common questions.

Technical guide to choosing the best SEO app for Shopify, evaluating impact on Core Web Vitals, indexation, and catalog scalability without technical errors.
Feb 7, 2026
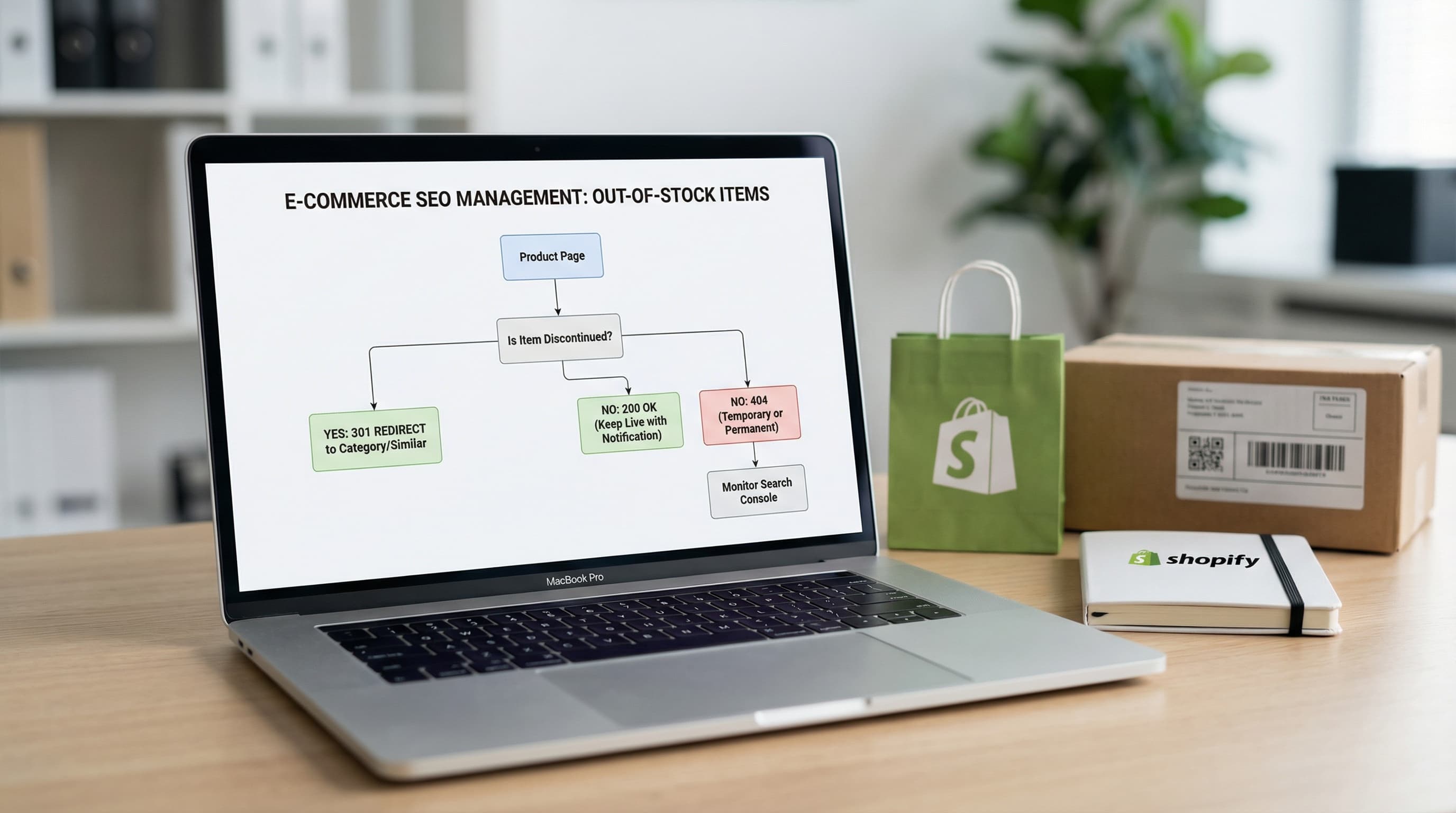
Learn how to manage discontinued products to avoid Soft 404 errors and maintain your authority with strategic 301 redirects.
Feb 2, 2026
Optimize your store navigation and improve rich results with this technical breadcrumb guide for Shopify.
Jan 24, 2026