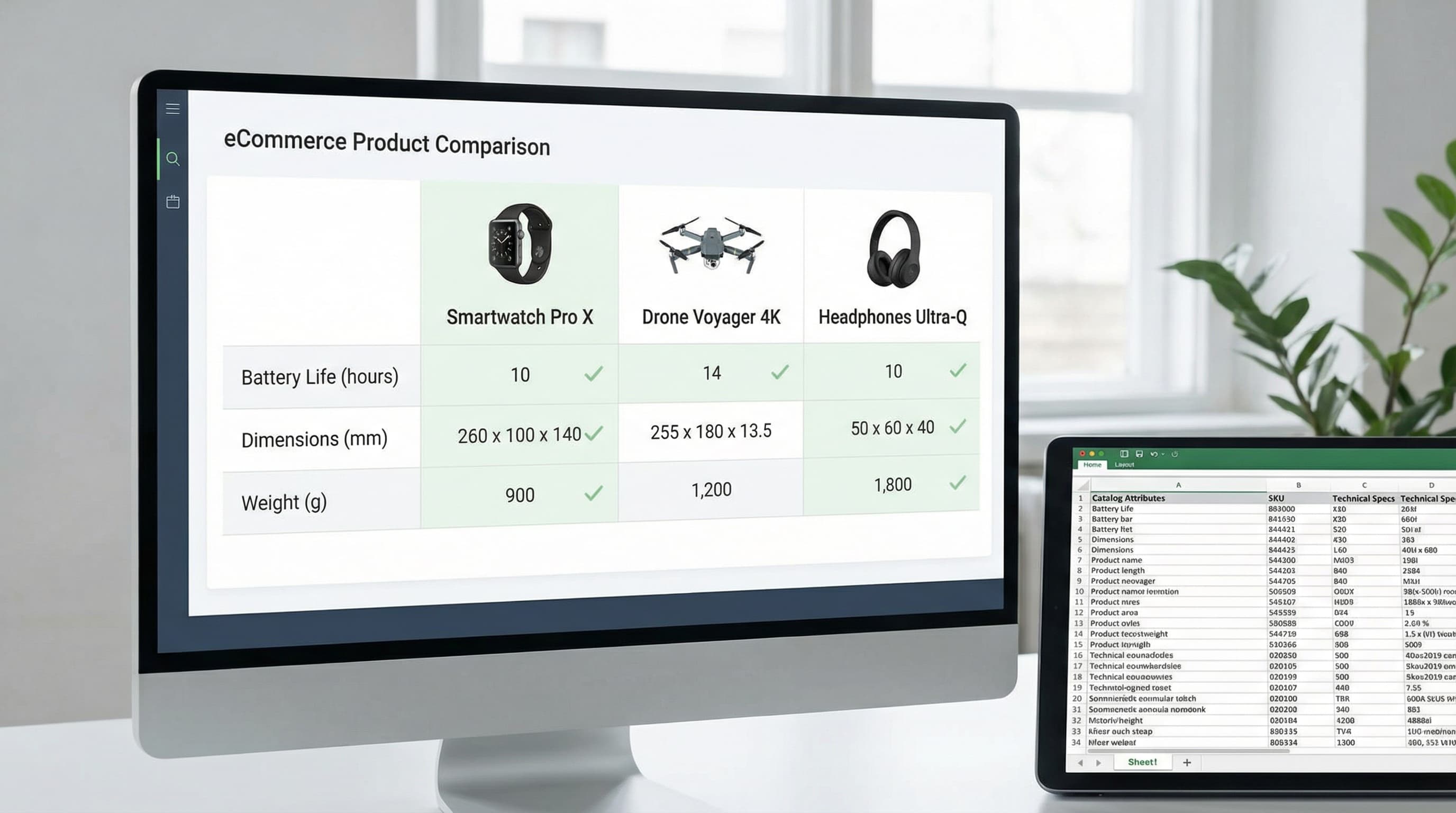
Building Scalable Ecommerce Product Comparison Tables
Stop manually updating static charts. A data-first playbook to building scalable, dynamic product comparison tables that drive conversion and reduce returns.
Feb 13, 2026
A field-by-field blueprint for mapping, generating, and auditing thousands of Amazon listings using structured data—without the manual chaos.
Amazon listing optimization at scale starts by mapping each internal product attribute to the exact Amazon field that influences indexing and conversion. This section breaks down which fields matter, how they interact with Amazon indexing, and why correct parent-child variation relationships are critical to avoid visibility drops.
Product title and bullet points are your primary on-page relevance signals for indexing and click-through. Backend search terms add indexable vocabulary not visible to shoppers. Parent-child variation families must use allowed variation themes so children do not get suppressed or lose independent indexing. For implementation patterns and variation templates, see a practical guide by Seller Candy.
Why this matters: The title is the strongest single-page relevance signal Amazon uses for both indexing and user click decisions.
How to approach: Build titles from canonical attributes using a template that places brand, model, key feature, size, and use in predictable slots. Enforce category length limits and avoid keyword stuffing by de-dupe rules at generation time. Use the title attribute from your PIM or master catalog as the source of truth so titles are repeatable across thousands of SKUs.
Why this matters: Bullets convert technical attributes into buyer-focused benefits and support additional indexable terms.
How to approach: Map three to five priority attributes from your product data model into benefit-oriented bullets. Use structured fields for materials, dimensions, and compatibility so copy generation remains deterministic. Keep bullets scannable and aligned with the title to avoid internal keyword cannibalization.
Why this matters: Backend search terms expand searchable vocabulary without harming conversion copy visible on the product page.
How to approach: Apply tokenization and de-duplication rules that remove words already present in title and bullets, include long-tail synonyms and alternate spellings, and respect character limits. Avoid punctuation and prohibited phrases. Treat backend fields as scarce index space that must be optimized per SKU using your catalog taxonomy and keyword research.
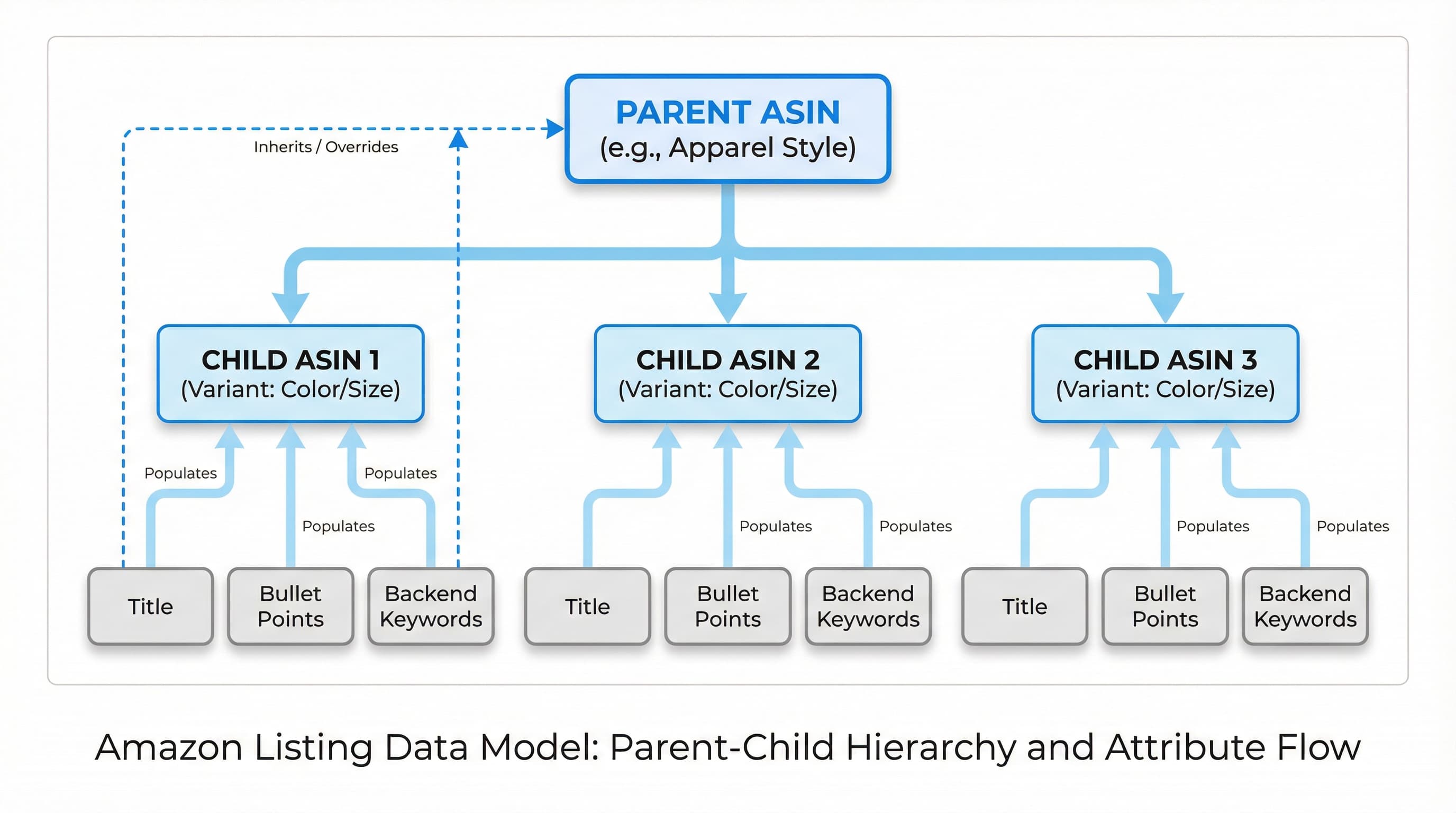
Why this matters: Correct parent-child relationships consolidate reviews and enable variant-specific indexing while preventing suppression or visibility loss.
How to approach: Use the correct variation theme allowed by category and create a non-purchasable parent record that acts as the anchor. Attach child SKUs that differ only in the allowed attributes. Validate brand and product type consistency across all children in your catalog export or flat file to avoid forced merges or delistings.
Amazon listing optimization starts with a deterministic map from internal product attributes to Amazon fields. This field-by-field blueprint explains how to build a source-of-truth attribute dictionary and an Amazon product listing template that powers automated generation, batch exports, and QA for thousands of SKUs.
Manual updates do not scale and cause inconsistent titles, bullets, and backend keywords across the catalog. A structured mapping enforces brand rules, prevents data drift, and unlocks automation for listing optimization, content operations, and catalog mapping. Consult Amazon rules and a practical feed automation example.
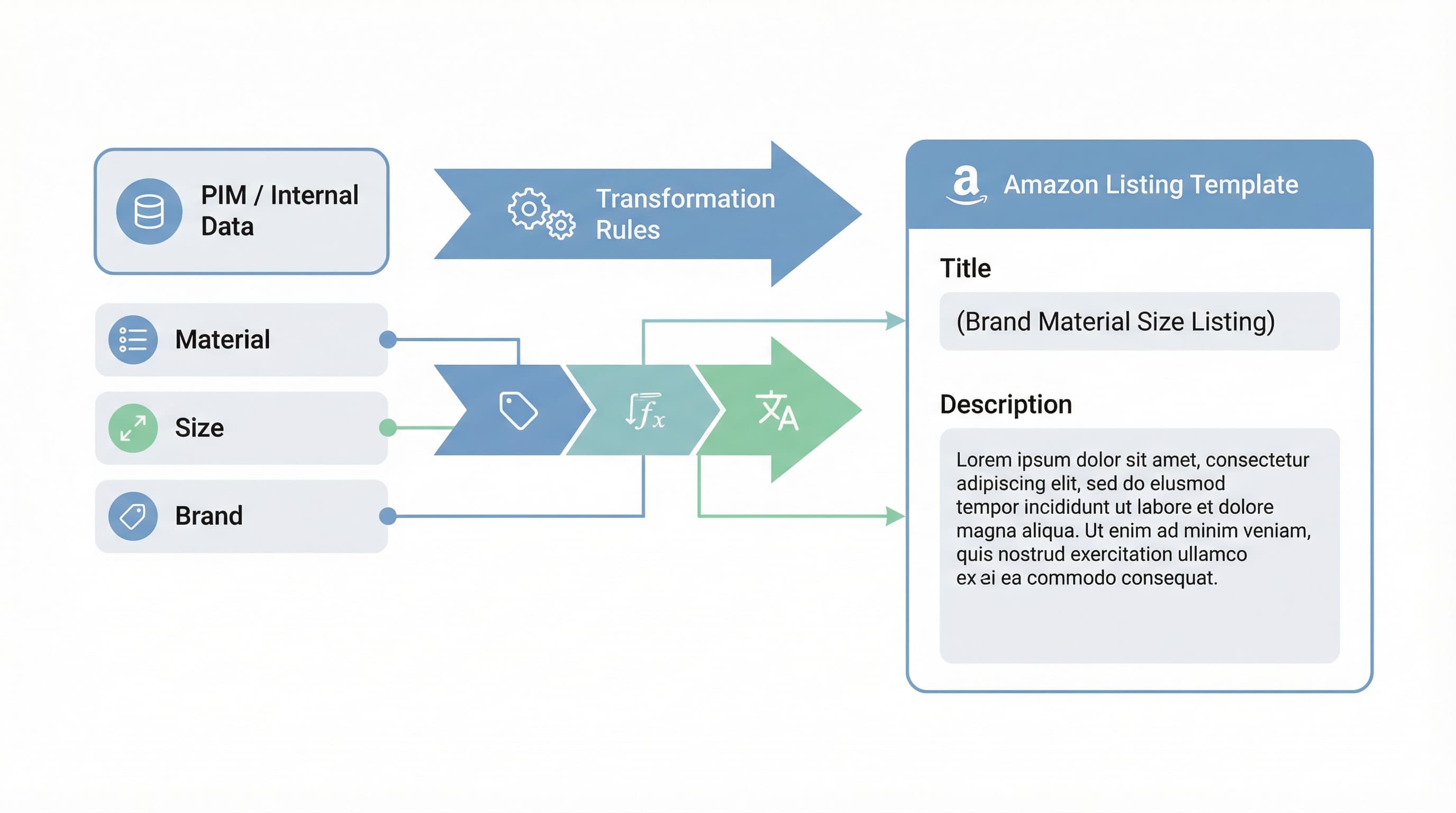
A shared attribute dictionary is the single source of truth.
sku_color maps to Amazon color_name (type: string, allowed values: red, blue, black).A template controls what fills title, bullets, description, images, and backend keywords.
Brand + Model + Key Feature + Size (Target max: 200 characters).Raw attributes need normalization and SEO enrichment.
material = "metal" and finish exists, create combined "material finish" token for title generation.Export automation must be paired with automated QA.
Tools and next steps: Use your PIM or a feed tool to manage mappings and automate exports. Start with a pilot and measure listing quality with the scorecard before scaling to thousands.
Amazon listing optimization at scale requires field-level formulas that map canonical attributes into titles, bullets, image instructions, variation rules, and backend keywords. This section shows a practical way to build category-specific rules, where AI is used for style harmonization and deduplication but not for business logic.
Segment by category and conversion band. Define short templates per field with slots and hard limits. Add conditional rules for variations and safety content. Use an automated QA scorecard before pushing to Seller Central. For official constraints, check Amazon product title guidance.
Mapping attributes to templates turns manual writing into repeatable output and reduces policy risk.
Create a template per category that defines slot order and priorities.
Brand + Model + KeyFeature + Wattage + Color.Use your PIM to provide normalized values. PIM is a product information management system used to store canonical attributes for each SKU. See a PIM primer for integration notes.
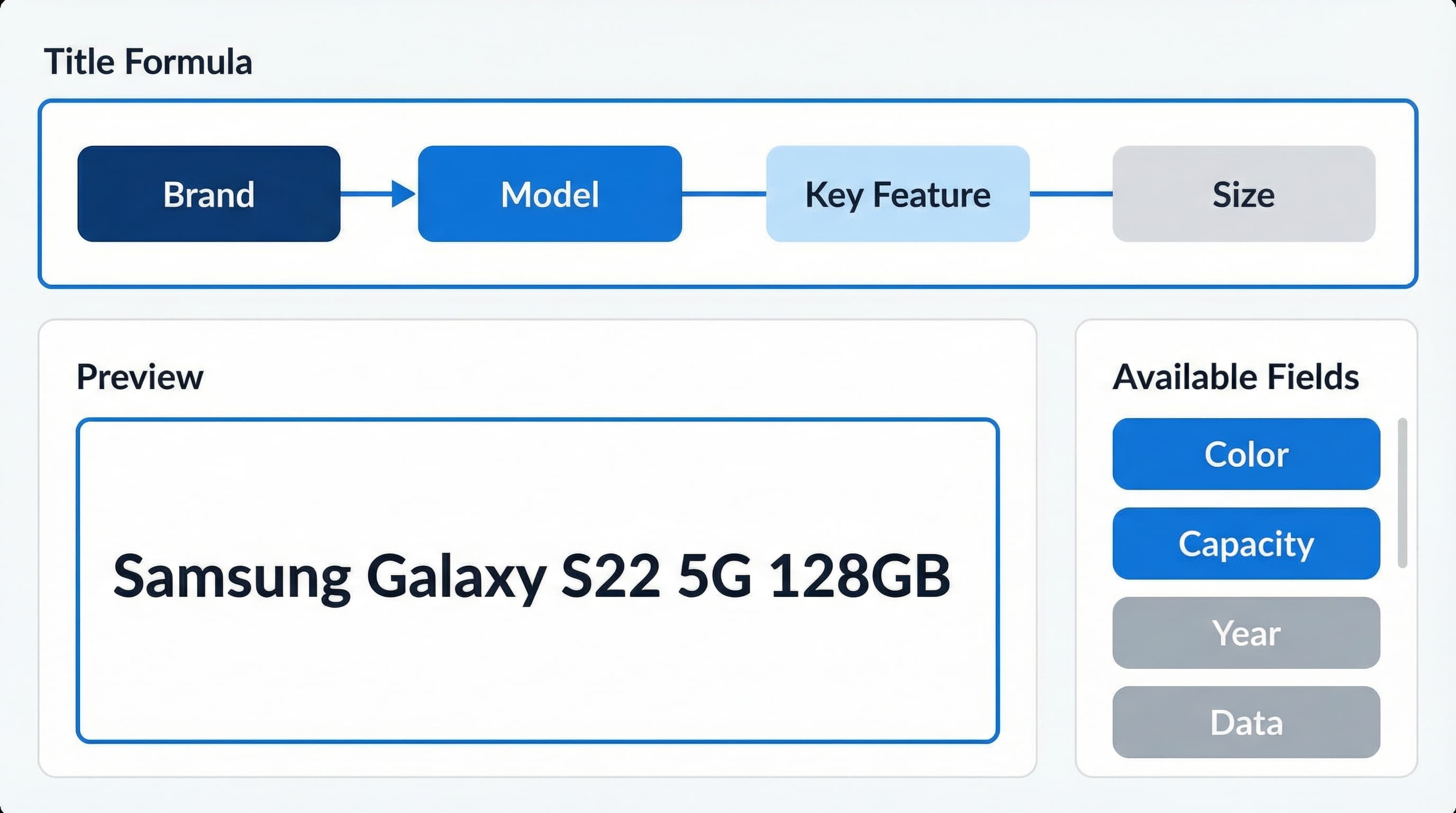
A single focused rule prevents length and policy violations.
Write a title pattern with mandatory and optional slots and a strict character cap. Add conditional rules so model or size only appear when present.
Brand + Model + KeyFeature + Size.Bullets are skimmable and must follow a predictable order for conversion.
Set bullet slots for primary benefit, usage, materials, care, and compliance. Limit each bullet to a max length and ban promotional qualifiers.
Automated checks catch scale problems before publish.
Run validations for title length, forbidden terms, backend keyword length, duplicate content, and image set completeness. Keep a weekly manual sample audit to catch false positives.
A Listing Quality Scorecard turns internal product attributes into a repeatable control that surfaces completeness gaps, compliance risk, and indexing hygiene across thousands of Amazon SKUs.
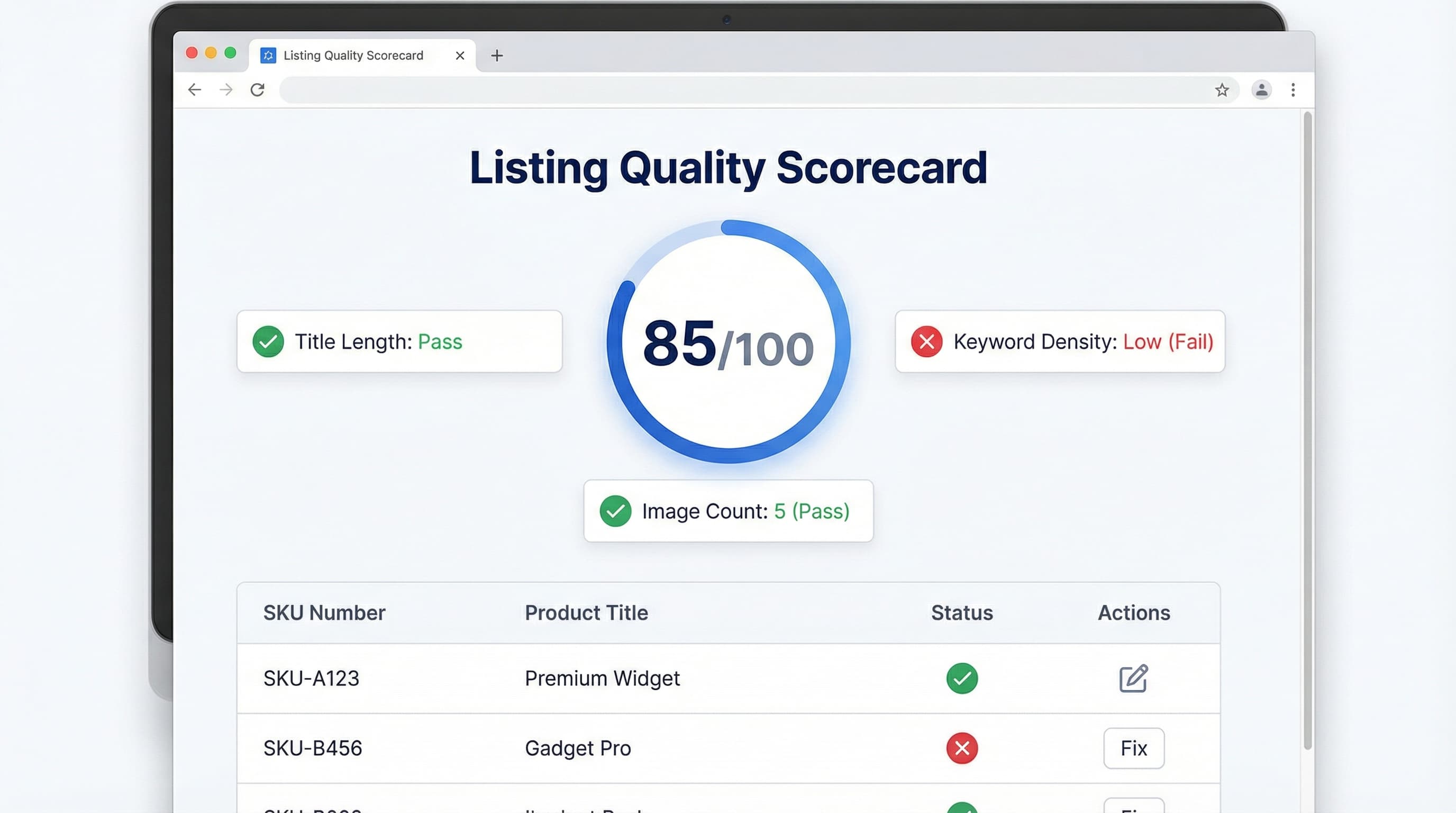
Context: PIM means product information management, centralizing product attributes for feeds. Seller Central is the compliance portal where updates are published.
The goal is a numeric Listing Quality Score that teams can filter and action across thousands of SKUs. Metrics drive prioritization and automation.
This defines representative checks so audits reveal systemic issues rather than lucky passes. Apply a stratified random sample by category, supplier, and lifecycle stage. Store the sample logic in a BI view or PIM export so audits are reproducible.
Completeness prevents avoidable listing failures and lost conversion. Implement validation rules in the PIM or ETL pipeline and capture pass/fail per field into the LQS.
Policy failures cause delisting and account actions. Use taxonomy mapping and regex-driven flags to detect prohibited claims, restricted brands, and wrong categories. Route flagged items to a manual review queue and record reviewer decisions for rule tuning.
Indexing checks verify that backend and visible fields are actually indexed and do not exceed limits. Run batch indexing tests for top search terms per SKU using a keyword tool and store indexing pass rates in the LQS. Fix backend search terms and recheck. See backend keyword best practices for detail.
Amazon listing optimization at scale requires a safe, repeatable feedback loop that turns wins into standards and flags regressions fast. This short field guide explains how to run controlled experiments, monitor suppressed ASINs, and use search term data to prioritize fixes so a catalog stays retail ready.
Controlled tests reveal which content fields move conversion without risking catalog health. Amazon Experiments is a Seller Central feature that runs controlled listing variants and compares customer response. It matters because it isolates the impact of one field change.
A suppressed ASIN stops buying activity quickly and is often fixable with a catalog-level rule.
product_feature from product_description.Search term trends show where content affects discoverability and SEO at scale.
Managing structured data, mapping attributes, and maintaining a high Listing Quality Score manually across thousands of SKUs is often the bottleneck that prevents growth. ButterflAI detects quality gaps and automates the generation and optimization of titles, descriptions, and backend keywords directly within your existing workflow.
ButterflAI connects to your catalog to enforce rules and leverage AI for scale, ensuring your listings remain compliant, indexed, and conversion-ready without the manual overhead.
Go deeper with guides and tools connected to this topic.
Quick answers to common questions.

Stop manually updating static charts. A data-first playbook to building scalable, dynamic product comparison tables that drive conversion and reduce returns.
Feb 13, 2026

Learn to diagnose, prioritize, and fix product feed errors to improve ROAS for Shopping and Performance Max campaigns.
Jan 30, 2026
Master your product data model, centralize attributes, and eliminate CSV chaos with an effective eCommerce PIM strategy.
Jan 27, 2026