How to Scale FAQ Schema Markup on Product Pages
Discover a governance-first workflow to create high-intent product FAQs from real customer data, deploy safely, and measure SERP CTR impact.
Feb 20, 2026
Technical guide to configuring Shopify Markets, avoiding duplicate content, and mastering global SEO with hreflang tags.

Success in international SEO on Shopify depends on ensuring that each localized version is shown to the right user without diluting domain authority. The hreflang attribute in Shopify signals to search engines the specific relationship between language and country variants, preventing equivalent versions from competing against each other for the same queries (cannibalization).
For technical specifications and official recommendations, consult the Google documentation on localized versions: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/specialty/international/localized-versions.
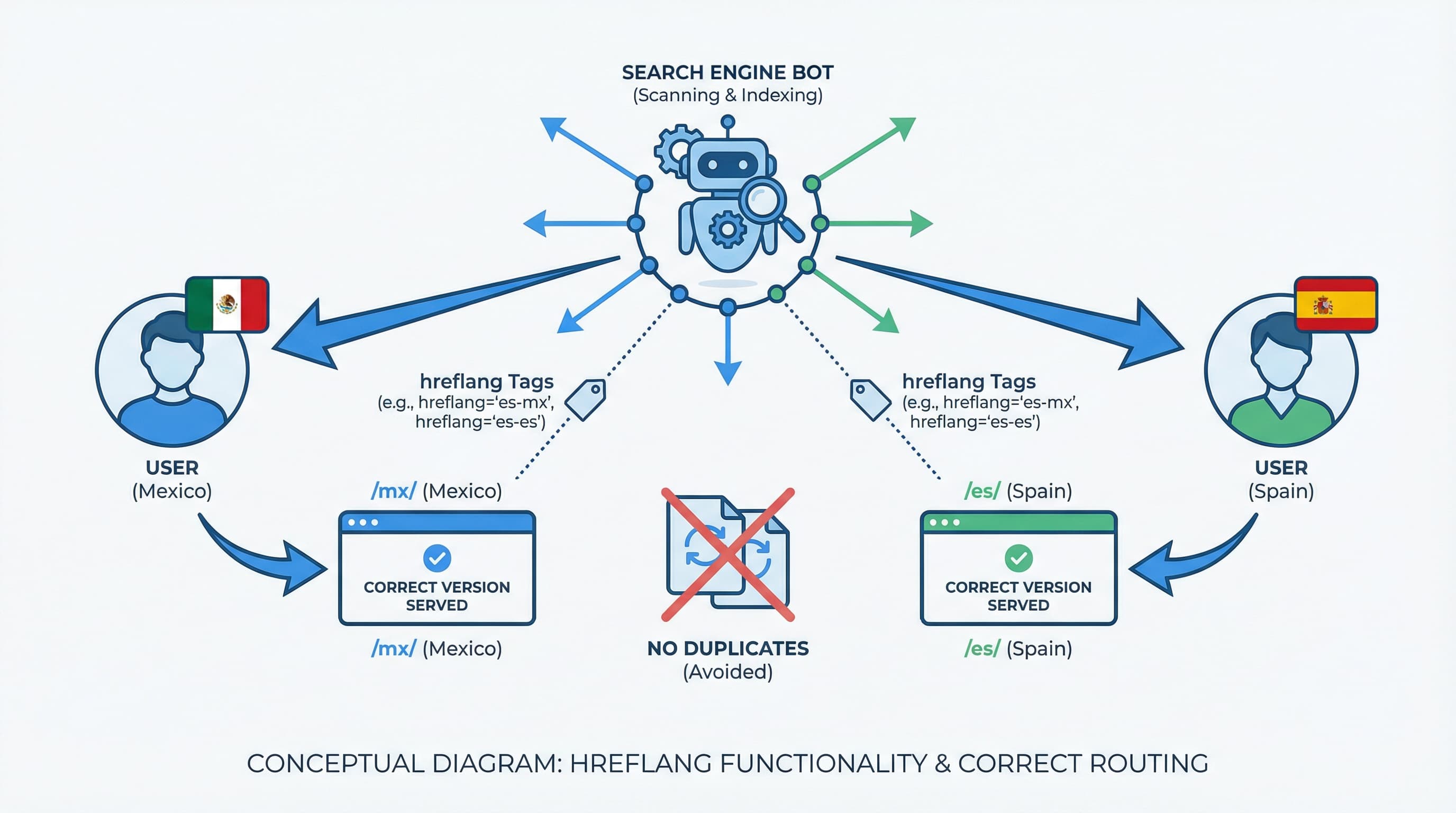
Why hreflang matters The main risk in multi-region stores is cannibalization and poorly geolocated traffic, where a user from Mexico ends up on the Spain store, resulting in bounces or logistical problems.
How to approach it
Generate and maintain a matrix of URL pairs per product or category that mandatorily includes the self-referencing URL. Implement hreflang via rel="alternate" tags in the <head> of every page or, alternatively, using hreflang entries in the XML sitemap. Subsequently validate in Google Search Console to detect non-reciprocal pairs (where A links to B, but B does not link to A) and language coding errors. Google Search Console is the essential tool for monitoring indexing and search errors, allowing you to identify hreflang issues before they affect performance.
Brief example
The correct structure of a tag is:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-ES" href="https://store.com/es/product" />
Typical error Omitting the self-referencing canonical URL or using incorrect language codes (e.g., using "eu" for Europe instead of a valid country code) causes broken pairs in validation.
Multiple implementation options exist depending on architecture and catalog volume.
How to approach it
/es, /fr) and add dynamic hreflang in theme.liquid templates.Brief example Use subfolders for markets with similar content and low logistical friction, and separate domains for top-tier markets with high investment and a need for strong local authority.
Typical error Not aligning canonical tags with hreflang generates contradictory signals and loss of visibility (e.g., canonical pointing to the global home while the hreflang points to the local variant).
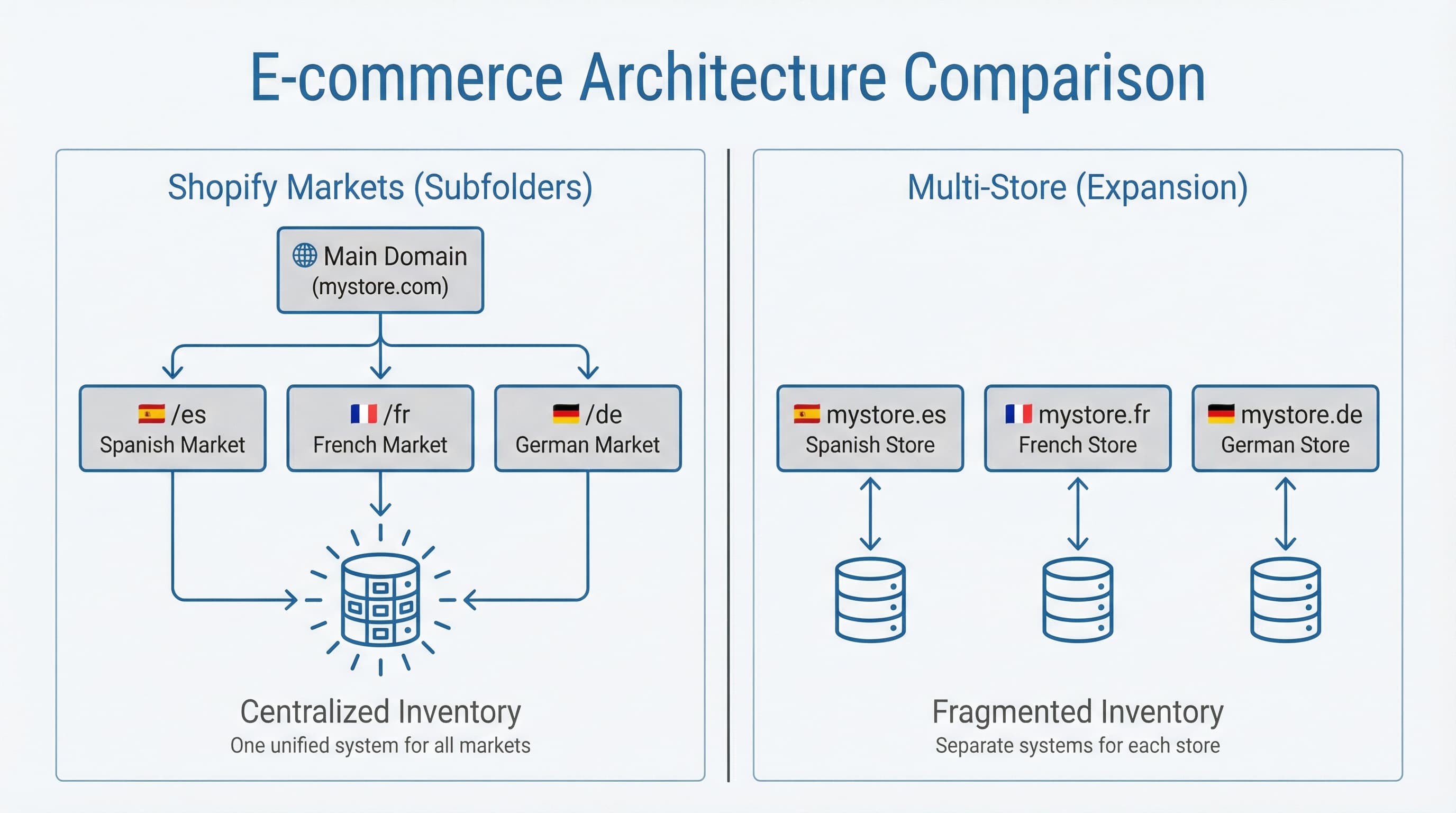
Starting internationalization without designing site architecture causes systemic indexing errors and hreflang misuse that is difficult to correct later. In this section, we compare Shopify Markets using subfolders versus the multi-store alternative so you can make the right decision based on SEO, operations, and logistics criteria.
Hreflang matters because it is the technical signal that indicates to search engines the geographic or linguistic version of a URL, avoiding contradictory indexing signals.
Why this step matters: The choice directly affects Domain Rating, technical maintenance, and Crawl Budget.
Approach: Evaluate SEO, logistics, and technical resources.
Example: A European store launching versions for France and Germany usually benefits from subfolders like domain.com/fr and domain.com/de to concentrate link signals and facilitate Shopify's automatic canonicalization.
Typical error: Choosing multi-store solely due to a local marketing team's preference without considering the loss of global authority and the exponential increase in technical maintenance costs.
Why this step matters: Domain authority is a key implicit factor in the distribution of link equity between international versions.
Approach: Prioritize subfolders if your goal is to climb SEO rankings quickly in new markets by leveraging the main market's authority. Configure Shopify Markets to serve content in subfolders and use hreflang to signal local versions. Shopify Markets documentation explains how to map domains and subfolders in the Markets panel (https://help.shopify.com/en/manual/markets).
Example: A strategy with domain.com/es and domain.com/en allows a PR campaign and links in Spain to indirectly improve the visibility of the English version if they are well linked internally.
Typical error: Creating subfolders without managing 301 redirects and proper canonicals, which generates massive duplicate content at launch.
Why this step matters: Operations and catalog structure determine if you need physical store separations beyond SEO.
Approach: Assess differences in pricing, inventory, and fulfillment.
Example: A retailer with independent warehouses and distinct legal/fiscal requirements for each country usually opts for multi-store to isolate checkout and invoicing processes.
Typical error: Ignoring the cost of ERP and PIM integration when planning a multi-store architecture, resulting in outdated product data.
Why this step matters: A clean technical implementation from day 1 drastically reduces errors in Search Console.
Approach: Implement hreflang based on the chosen architecture.
Example: Generate a sitemap per language that includes all local URLs and submit it to Search Console for each domain property or URL prefix.
Typical error: Relying only on IP-based geolocation redirects to signal language without using hreflang attributes and canonicals, which prevents Googlebot (which usually crawls from the US) from seeing local versions.
The goal of this section is to describe how to configure hreflang in Shopify to avoid international SEO issues and minimize duplicate content. We explain URL requirements, canonical tag treatment, and strategy for sitemaps and x-default.
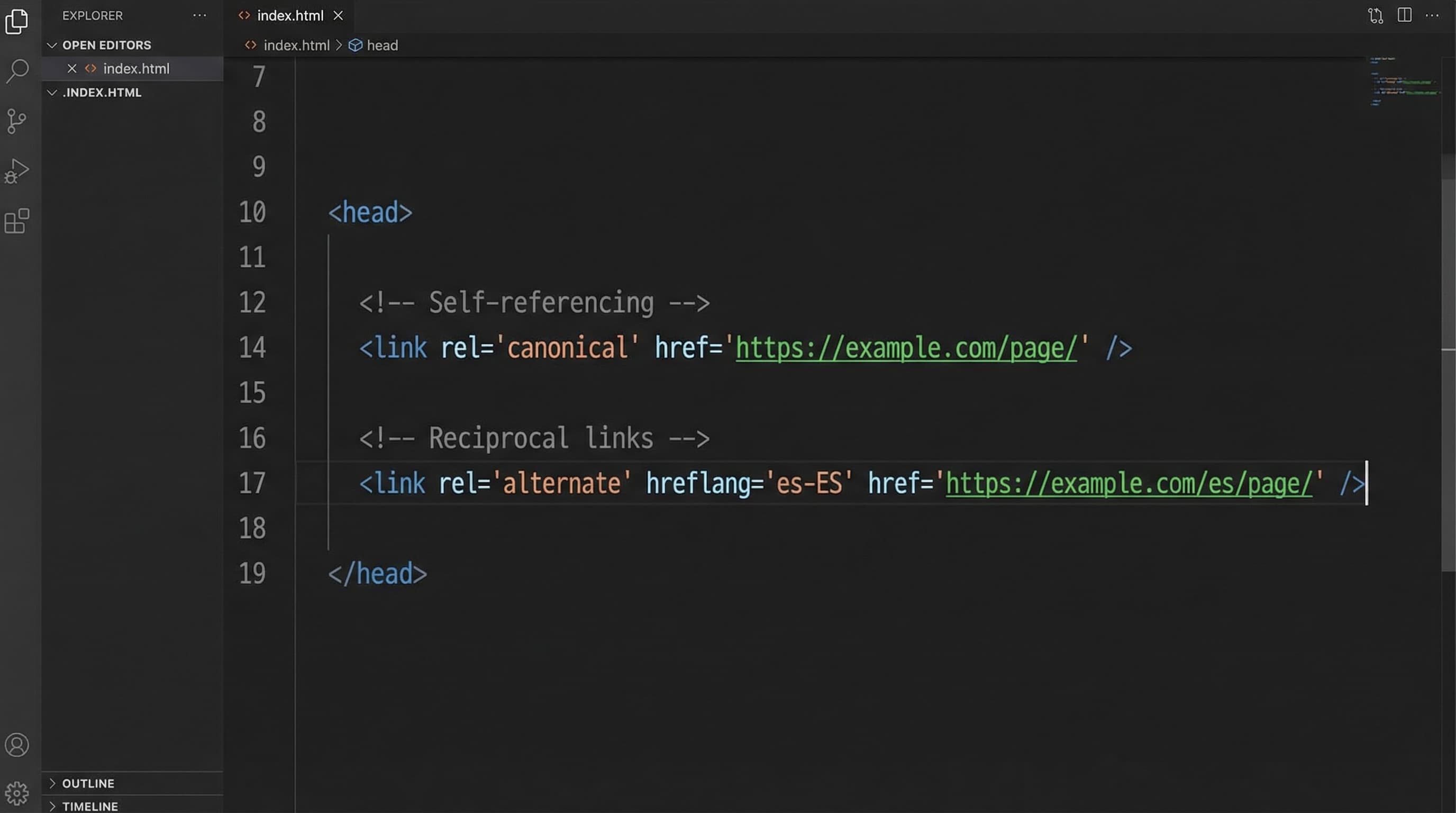
Before diving into details, ensure your regional versions meet three basic rules:
Shopify Markets allows serving versions by country or language via distinct domains, subdomains, or subfolders. Each variant must have its own URL for rel="alternate" hreflang="x" tags to work correctly.
In Shopify stores, the platform can generate rel="alternate" tags automatically if you activate markets and associated domains, but it is vital to control canonical consistency to avoid loops. Using a PIM (Product Information Management) helps centralize product attributes and generate consistent URLs. Product Feeds help maintain coherence between versions in sitemaps and marketplaces. Shopify Metafields allow mapping specific information per variant (e.g., translated descriptions or local specs), improving metadata quality.
Why this step matters Stable and unique URLs prevent Google from considering regional versions as duplicate content and allow for correct value attribution.
How to approach it
Choose a URL strategy and apply it globally. Valid options: country domains (ccTLD), subdomains, or subfolders. Avoid at all costs using URL parameters to define language (e.g., ?lang=fr). In Shopify Markets, configure domains and subfolders from the admin and ensure the main store does not dynamically rewrite URLs without control.
Example
example.es for Spain and example.fr for France.mydomain.com/fr/ for the French market.Typical error Mixing subdomain and subfolder for the same region without mapping the canonical correctly, splitting link strength.
Why this step matters An incorrect canonical can override hreflang tag instructions, causing Google to ignore the local version and index only the main version.
How to approach it
Whenever you publish alternative versions, each variant must declare a rel="canonical" tag pointing to its own URL (self-referencing). rel="alternate" hreflang tags must be present in every version and list all variants, including the page itself. Never point the canonical to the main (global) version if you want the local version to rank, unless the content is 100% identical and you prefer to consolidate.
Example
In the Spanish version (/es/product), the page includes:
rel="canonical" pointing to .../es/productrel="alternate" listing: es, fr, en, x-default.Typical error
Leaving a hardcoded global canonical pointing always to the main domain root (.com) from all local variants.
Why this step matters
Sitemaps allow declaring alternates without cluttering HTML code (useful for load times), and the x-default attribute designates a fallback version for users whose language does not match any specific version.
How to approach it
Include xhtml:link rel="alternate" entries in the sitemap for each regional URL or publish an independent sitemap per market. Use x-default to point to a global page or a neutral language/country selector.
Example
A sitemap including <loc>url_es</loc> and <loc>url_fr</loc> with their respective nested alternate tags, and an x-default entry pointing to the international home (.com) or a country selection page.
Typical error
Not including x-default when a language or geolocation selector exists, leaving users from "undefined" markets without a clear destination for Google.
Include all domains and subdomains (if using URL prefixes) for each market in Search Console. Use the URL Inspection tool to verify which version Google is selecting as canonical. Review the "International Targeting" report (if available in legacy) or indexing reports.
Quick implementation checklist:
rel="alternate" hreflang present in every version.x-default entries configured for non-matching traffic.This section details a practical process for auditing and correcting hreflang tags in Shopify stores, focusing on detecting recurring errors at scale to avoid organic traffic losses.
TL;DR of the audit process:
rel="alternate" presence.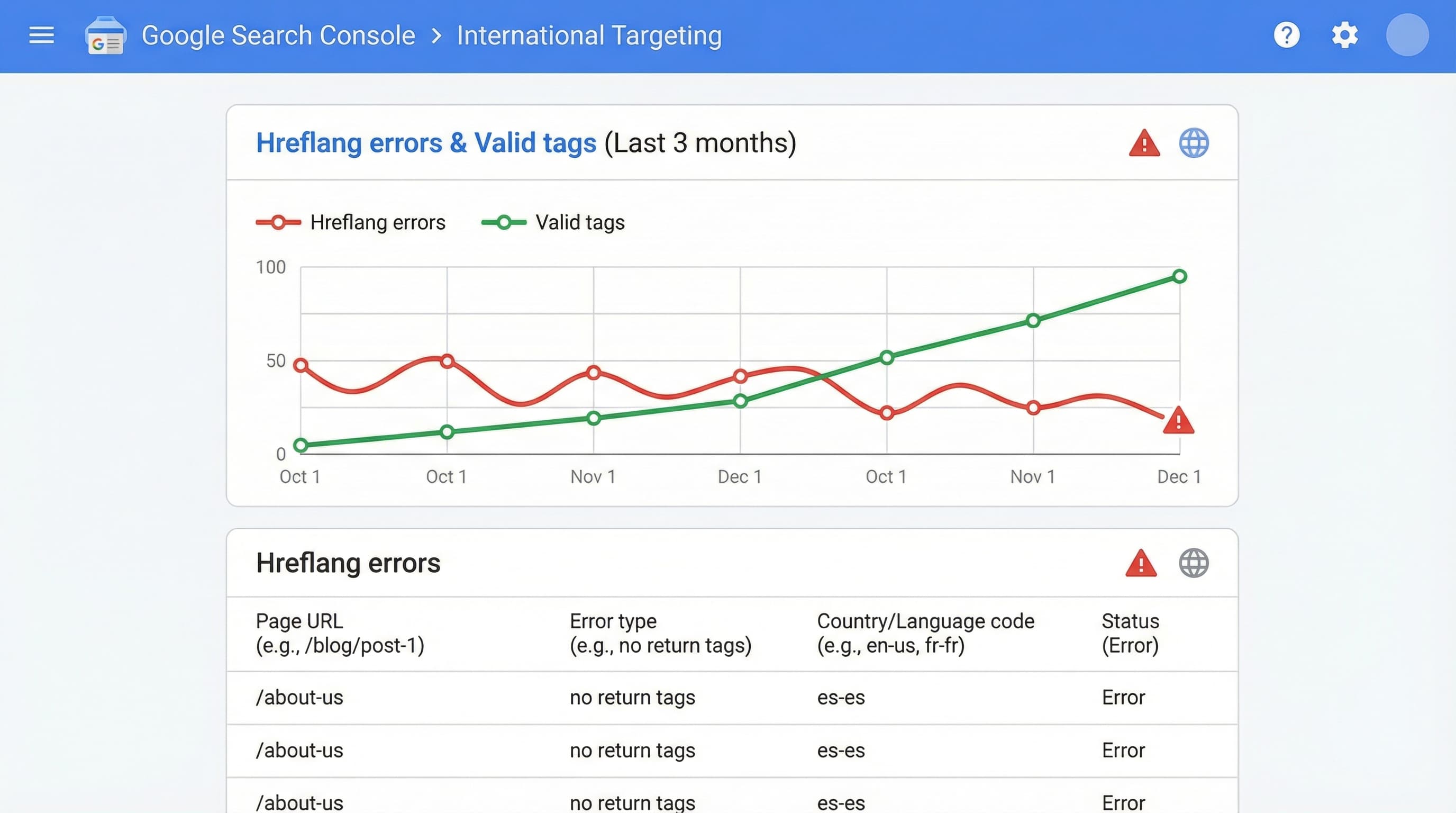
Context: This is the most direct and reliable way ("source of truth") to locate broken tags and targeting errors perceived by Google.
How to approach it: Access the international targeting or indexing report in Search Console and export the error list. Filter by common types: "hreflang not found" (missing reciprocal tag), "Alternate URL with 404 response," and "Inconsistent tags. " Use individual URL inspection for critical cases.
Brief example: Export a CSV with columns URL, Error, and Priority, and focus first on resolving the 50 URLs with the highest number of affected impressions.
Typical error: Not manually checking that the alternate URL responds with a 200 OK code before marking the fix in GSC.
Context: Auditing thousands of pages (SKUs) requires automated batch checks, not manual ones.
How to approach it: Run a crawler (like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb) that traverses product and collection paths, and parses the <head> for rel="alternate" links. Configure the tool to extract the HTTP status code of each alternate URL and its canonical. If you manage the catalog from a PIM, export the master list of handles and compare. In stores with subfolders, review redirect chains that may cause timeouts.
Brief example: A script or crawler configuration that returns for each URL: Status Code, Hreflang Count, List of Alternates, and Redirect Chain.
Typical error: Infinite redirect loops between versions (e.g., ES redirects to EN, and EN redirects to ES) caused by poorly applied IP detection rules.
Context: Exact matching between what is declared in the sitemap and what is present on-page avoids contradictory signals that confuse the crawler and waste crawl budget.
How to approach it: Download the sitemap index and extract child sitemaps by language. Generate two lists (Sitemap vs. Actual Crawl) and calculate the difference (diff). Mark URLs appearing only in the sitemap and those containing rel="alternate" on the page but not in the XML. If using Shopify Markets, check if there are unpublished products in a specific market that still appear in the general sitemap.
Brief example: Use a simple spreadsheet comparison (VLOOKUP) between both lists to generate a "Mismatch" report.
Typical error: Sitemaps with old URL versions that do not reflect recent migrations or handle changes in Shopify.
Rel="alternate" and rel="canonical" must not contradict each other.In this section, we address "gray area" issues that often go unnoticed in automated audits but severely affect performance, such as currency selectors and business logic conflicts.
Context: Automatic selectors (pop-ups or forced redirects) can change the URL or visible content via JavaScript and confuse Googlebot.
Approach: Confirm that currency or country selection does not depend exclusively on cookies or JavaScript that modifies the DOM without reflecting it in a distinct URL. In Shopify Markets, automatic country redirects can create loops or prevent the bot from accessing secondary versions. Always prefer versions with distinct URLs (subfolders/domains) and use x-default for the selection page.
Brief example: Keep store.com/es accessible for any IP, instead of forcing a redirect to store.com/us if you detect an American IP (Googlebot usually crawls from the US).
Typical error: Implementing an automatic 302 redirect based on IP without offering a crawlable alternative route.
Context: Hreflang communicates alternatives; canonical defines preference. If they clash, Google may ignore hreflang for safety.
Approach: Ensure that each localized URL includes hreflang tags for all versions in its <head> and that the canonical tag of that URL points strictly to itself. In multi-store setups with distinct domains, replicate the full hreflang block on each domain or use a cross-domain sitemap listing alternates to avoid code dependencies in the theme.
Brief example: A page at store.com/es must have:
store.com/esstore.com/es, store.com/en, x-default.Typical error: Global canonical pointing to the root homepage, effectively deindexing localized deep pages.
Context: The chosen structure affects geographic signals and long-term catalog operational management.
Approach:
.de for Germany).Brief example: store.com (Global) and store.com/es (Spain) must be listed in a unified multi-region sitemap or in sitemaps linked in robots.txt.
Typical error: Relying only on metatags in the code and forgetting to include versions in the XML sitemap.

Managing the consistency of thousands of URLs, localized product attributes, and hreflang tags across multiple markets in Shopify often leads to manual errors and data desynchronization.
ButterflAI detects inconsistencies in your catalog and automatically generates optimized content and necessary metadata for each market. By centralizing optimization, you ensure that international expansion doesn't break your SEO architecture, allowing scaling to new countries without multiplying the team's operational load.
Go deeper with guides and tools connected to this topic.
Quick answers to common questions.

Discover a governance-first workflow to create high-intent product FAQs from real customer data, deploy safely, and measure SERP CTR impact.
Feb 20, 2026
Technical guide to choosing the best SEO app for Shopify, evaluating impact on Core Web Vitals, indexation, and catalog scalability without technical errors.
Feb 7, 2026
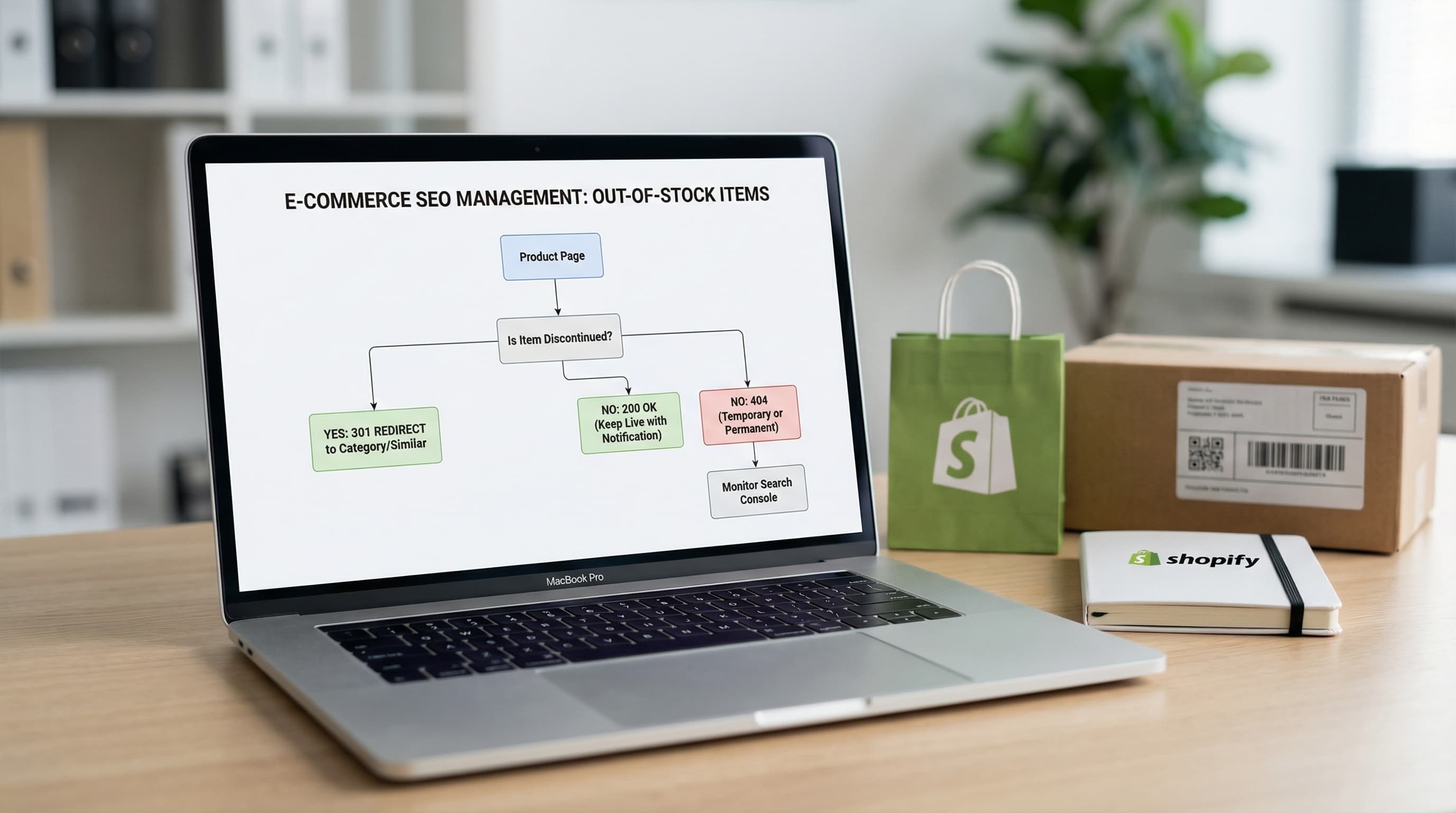
Learn how to manage discontinued products to avoid Soft 404 errors and maintain your authority with strategic 301 redirects.
Feb 2, 2026